Overview
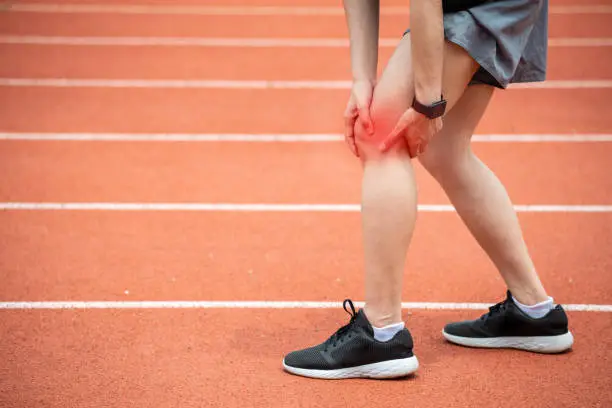
Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS) is widely recognized as one of the most frequent overuse injuries seen in athletes and active individuals. It primarily affects the lateral (outer) aspect of the knee and thigh and is especially common in runners, cyclists, hikers, and anyone who performs repetitive lower-limb movements for extended periods. Because the knee functions as a complex hinge between the hip and ankle, repetitive stress can easily overload the structures on its outer side, making iliotibial band syndrome a frustrating and sometimes performance-limiting condition.
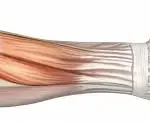
The iliotibial band itself is a dense, fibrous band of fascia that originates from the iliac crest at the hip and travels down the outside of the thigh before inserting into the tibia at a site called Gerdy’s tubercle. Along its course, it blends with fibers of the gluteus maximus and tensor fasciae latae (TFL), which means it plays a dual role in both movement and stability. During walking, running, climbing stairs, or squatting, this band helps stabilize the knee laterally, assists in controlling hip motion, and transfers force between the hip and the lower leg. In essence, it is a vital link in the kinetic chain of the lower limb.
When this band becomes excessively tight, inflamed, or irritated — most commonly from repeated friction where it passes over the lateral femoral epicondyle (the bony prominence on the outside of the knee) — the result is iliotibial band syndrome. Initially, athletes may feel a mild ache or tightness after activity, but if the problem is ignored, it can escalate to sharp pain, swelling, and an inability to continue running or training. Left untreated, it may even interfere with everyday movements like walking, sitting for long periods, or getting up from a chair.
At DMPhysios, a renowned clinic located in Noida specializing in spine and sports conditions with a strong focus on patient-centered rehabilitation, individuals suffering from iliotibial band syndrome receive thorough assessments, evidence-based treatments, and highly individualized rehabilitation plans. This approach not only helps them return safely to their sport or routine but also reduces the risk of future recurrences by addressing the underlying causes.
Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of iliotibial band syndrome early helps in prompt treatment and prevents chronic pain:
- Lateral Knee Pain: The hallmark symptom is sharp or burning pain on the outer side of the knee, especially during running, descending stairs, or cycling.
- Tenderness on Palpation: Pain or tenderness along the lateral femoral epicondyle or along the iliotibial band.
- Pain During Activity: Pain typically starts after a certain distance or time into activity and may subside with rest initially but can become constant if untreated.
- Swelling: Mild swelling or a snapping sensation at the lateral knee may occur.
- Pain Radiating Up the Thigh: In severe cases, discomfort may extend toward the hip or outer thigh.
DMPhysios emphasizes a thorough assessment of these symptoms to differentiate iliotibial band syndrome from other conditions like lateral meniscus tears or patellofemoral pain syndrome.
Types of Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Although iliotibial band syndrome is generally classified as a single entity, clinicians sometimes distinguish between:
- Acute Iliotibial Band Syndrome – Short-term irritation or inflammation often triggered by a sudden increase in activity or training errors.
- Chronic Iliotibial Band Syndrome – Long-standing pain due to ongoing biomechanical issues, repetitive strain, or untreated acute symptoms.
At DMPhysios, identifying whether the patient is in the acute or chronic stage of iliotibial band syndrome allows for a more targeted rehabilitation approach.
Causes
The development of iliotibial band syndrome is multifactorial. Some common causes include:
- Overuse: High-mileage running, cycling, or repetitive squatting without adequate rest.
- Training Errors: Sudden increase in distance, intensity, or frequency of workouts.
- Downhill Running: Increases knee flexion angles, amplifying friction of the iliotibial band over the lateral femur.
- Improper Footwear: Worn-out shoes or inadequate support can change lower-limb biomechanics.
- Surface Camber: Running on banked or sloped roads causes uneven strain on the iliotibial band.
DMPhysios clinicians pay close attention to training history and environmental factors when evaluating patients with iliotibial band syndrome.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing iliotibial band syndrome:
- Biomechanical Issues: Excessive foot pronation, leg-length discrepancies, or hip muscle weakness.
- Tight Iliotibial Band: Reduced flexibility increases friction.
- Weak Hip Abductors: Particularly the gluteus medius, leading to poor pelvic stability.
- Gender: Some studies suggest higher incidence in female runners due to wider pelvis and increased Q-angle.
- Previous Injury: History of knee or hip injury can predispose to ITBS.
At DMPhysios, a detailed biomechanical assessment is a cornerstone of evaluating risk factors for iliotibial band syndrome, ensuring long-term prevention strategies.
Treatment
Initial management of iliotibial band syndrome focuses on reducing pain and inflammation, followed by addressing underlying biomechanical and training factors.
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Reducing or stopping aggravating activities such as running or cycling temporarily to allow tissues to heal.
2. Ice Therapy
Applying ice packs to the lateral knee for 15–20 minutes several times a day to reduce inflammation.
3. Anti-inflammatory Measures
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help in acute phases, as recommended by a physician.
4. Stretching and Foam Rolling
Gentle stretches and foam rolling of the iliotibial band, glutes, and quadriceps can alleviate tension.
5. Correcting Training Errors
Gradual progression of mileage, avoiding excessive downhill running, and checking footwear.
DMPhysios integrates all these elements into a customized care plan for patients with iliotibial band syndrome.
Physiotherapy Treatment
Physiotherapy is the cornerstone of both acute and chronic iliotibial band syndrome management. At DMPhysios in Noida, patient-centered rehabilitation ensures every program is tailored to the individual’s needs, lifestyle, and sport.
1. Comprehensive Assessment
A physiotherapist at DMPhysios performs a detailed evaluation including gait analysis, hip and knee strength testing, flexibility assessments, and training review to pinpoint the root cause of iliotibial band syndrome.
2. Manual Therapy
- Soft Tissue Mobilization: Targeting the iliotibial band, tensor fasciae latae (TFL), and lateral thigh muscles to reduce tension.
- Trigger Point Release: Alleviates pain and improves tissue pliability.
- Joint Mobilizations: If hip or knee restrictions are present, gentle mobilizations restore movement.
3. Specific Stretching
- IT Band Stretch: Crossing the affected leg behind the other and leaning away to stretch the lateral thigh.
- TFL and Gluteal Stretches: Reduce tension on structures contributing to ITBS.
4. Strengthening Exercises
Weak hip abductors and external rotators are a major cause of iliotibial band syndrome. DMPhysios physiotherapists progress patients through a structured strengthening program:
- Side-Lying Hip Abduction
- Clamshells
- Monster Walks with Resistance Bands
- Single-Leg Deadlifts
- Step-Downs or Lateral Step-Ups
These exercises improve pelvic and knee control, reducing excessive strain on the iliotibial band.
5. Neuromuscular Re-Education
Teaching proper running form, improving cadence, and retraining landing mechanics to reduce lateral knee stress.
6. Taping or Bracing
Kinesio taping or supportive strapping may be used to offload the iliotibial band temporarily during rehabilitation.
7. Gradual Return to Sport
Once pain subsides and strength improves, DMPhysios physiotherapists guide patients through a stepwise return-to-running or sport-specific drills to ensure a safe comeback.
8. Patient Education
Understanding training errors, footwear choices, and the importance of warm-up and cool-down routines is essential for long-term prevention of iliotibial band syndrome.
This multi-dimensional approach at DMPhysios ensures not only symptom relief but also correction of underlying causes, reducing the risk of recurrence.
Prevention
Preventing iliotibial band syndrome is achievable with consistent attention to training and biomechanics:
- Gradual Training Progression: Avoid sudden increases in running mileage or cycling intensity.
- Proper Footwear: Replace shoes regularly and ensure correct fit for your foot type.
- Strength Training: Focus on hip abductors, glutes, and core muscles to maintain pelvic stability.
- Stretching and Foam Rolling: Incorporate regular stretching of the IT band and surrounding muscles.
- Cross-Training: Include low-impact activities like swimming or elliptical training to reduce repetitive stress.
- Surface Awareness: Avoid excessive running on sloped roads or always running in one direction on a track.
DMPhysios provides preventive workshops and individualized exercise programs for athletes and active individuals in Noida, aiming to reduce the incidence of iliotibial band syndrome and other overuse injuries.
Conclusion
Iliotibial band syndrome is a common but preventable overuse injury affecting athletes and active individuals. Early recognition of symptoms, prompt management of pain and inflammation, and addressing underlying biomechanical factors are key to full recovery.
At DMPhysios, a premier clinic located in Noida for spine and sports conditions that offers patient-centered rehabilitation, individuals with iliotibial band syndrome receive holistic, evidence-based care. Through detailed physiotherapy assessment, manual therapy, strengthening, and patient education, DMPhysios not only treats the current injury but also equips patients with tools to prevent recurrence.If you’re experiencing lateral knee pain or suspect iliotibial band syndrome, don’t wait for it to worsen. Book an appointment at DMPhysios today to start your personalized rehabilitation program and get back to your sport or activity safely.