Overview
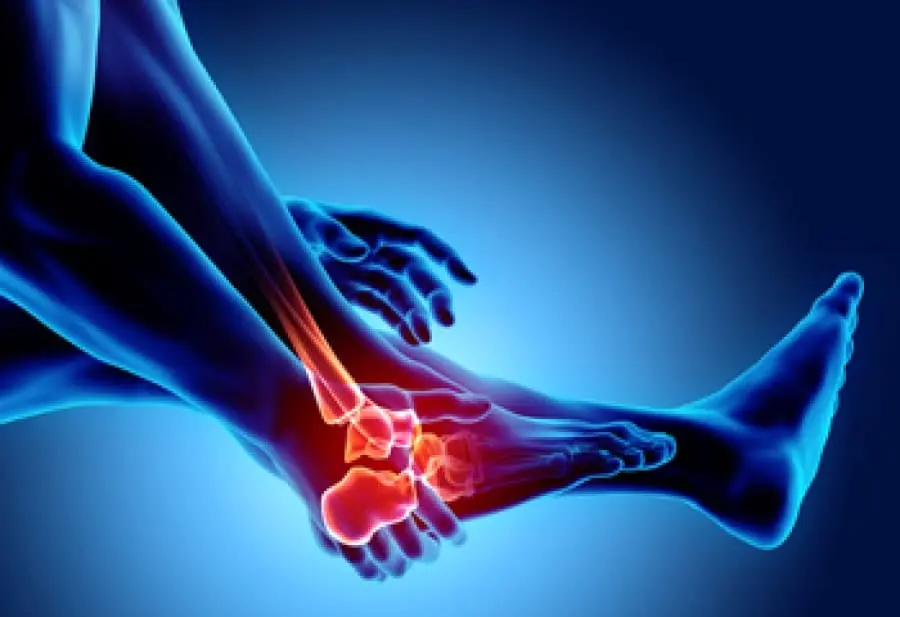
Tarsal Coalition is a condition that occurs when two or more tarsal bones in the foot are abnormally connected by bone, cartilage, or fibrous tissue. The tarsal bones form the back portion of the foot and are essential for proper movement, flexibility, and weight-bearing. When these bones are fused, either partially or completely, the foot loses its normal range of motion. This often results in stiffness, pain, instability, and difficulty with daily or sports-related activities.
Although Tarsal Coalition may be present from birth, many individuals do not experience symptoms until adolescence, when the bones begin to mature. For some, this condition can remain asymptomatic, while for others it can cause significant functional limitations and chronic pain. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and effective treatments is crucial in ensuring a better quality of life for those affected.
At DMPhysios, a trusted clinic in Noida specializing in spine and sports conditions with patient-centered rehabilitation, we emphasize early diagnosis and comprehensive physiotherapy management to help patients regain foot function and return to an active lifestyle.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Tarsal Coalition vary depending on the severity of the bone connection, but common signs include:
- Foot pain (often in the hindfoot or midfoot, worsened by activity)
- Stiffness in the ankle or foot
- Limited range of motion, especially during inversion and eversion movements
- Frequent ankle sprains due to instability
- Flatfoot deformity (rigid flatfoot that doesn’t improve on tiptoe)
- Fatigue in legs or feet after walking or standing for prolonged periods
- Difficulty in sports or running due to pain and lack of mobility
Pain typically becomes noticeable in late childhood or early adolescence, as bone maturation increases stress at the coalition site. Some individuals may also experience limping or avoidance of weight-bearing on the affected foot.
Types of Tarsal Coalition
There are different types of Tarsal Coalition, classified based on the bones involved and the type of tissue forming the connection:
- Calcaneonavicular Coalition
- Occurs between the calcaneus (heel bone) and the navicular bone.
- This is one of the most common types, often detected in adolescents.
- Talocalcaneal Coalition
- Involves fusion between the talus and calcaneus bones.
- Frequently causes pain and stiffness, limiting subtalar joint motion.
- Talonavicular and Calcaneocuboid Coalition
- Less common, but can still lead to functional problems in foot biomechanics.
- Complete vs. Incomplete Coalition
- Some coalitions are complete bony fusions, while others are formed from fibrous or cartilaginous tissue.
- The severity of symptoms depends largely on the degree of fusion.
Causes
The most common cause of Tarsal Coalition is congenital development, meaning it is present at birth due to improper segmentation of bones during fetal growth. However, symptoms usually do not present until later childhood or adolescence.
Other causes include:
- Genetic factors – Family history of Tarsal Coalition increases the likelihood of inheritance.
- Post-traumatic injury – Severe ankle or foot trauma can sometimes lead to abnormal bone healing and coalition.
- Infections or arthritis – Rarely, chronic infections or inflammatory joint conditions can contribute to coalition formation.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing Tarsal Coalition:
- Genetic predisposition – If one or both parents have the condition.
- Adolescence – Symptoms usually appear between ages 9–16, when bones begin to harden.
- High activity levels – Athletes or active children may notice symptoms earlier due to increased stress on the foot.
- Flatfoot deformity – Existing biomechanical imbalances can worsen symptoms.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and the extent of the coalition. Options include:
- Conservative (Non-Surgical) Management
- Rest and activity modification
- Anti-inflammatory medications for pain relief
- Orthotics or arch supports to reduce stress on the foot
- Casting or immobilization in severe flare-ups
- Surgical Treatment
- If conservative methods fail, surgical resection of the coalition may be performed.
- In some cases, fusion surgery may be required to stabilize the foot.
At DMPhysios, the focus is always on conservative, patient-centered rehabilitation before considering surgical options.
Physiotherapy Treatment
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in managing Tarsal Coalition by reducing pain, improving mobility, and preventing future complications. At DMPhysios in Noida, physiotherapy programs are tailored individually, ensuring that patients regain both function and confidence.
1. Pain Management Techniques
- Cryotherapy and heat therapy for pain relief and stiffness.
- Ultrasound therapy to reduce inflammation at the coalition site.
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) for pain modulation.
2. Stretching Exercises
Improving flexibility is essential in managing foot stiffness:
- Calf stretches to ease tension in the Achilles tendon.
- Plantar fascia stretches to maintain foot arch mobility.
- Ankle inversion and eversion stretches to improve subtalar joint flexibility.
3. Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the muscles around the ankle and foot helps compensate for restricted movement:
- Theraband resisted ankle movements (inversion, eversion, dorsiflexion, plantarflexion).
- Toe curls and towel scrunches to activate intrinsic foot muscles.
- Heel raises to strengthen calf muscles and support arch stability.
4. Balance and Proprioception Training
Since Tarsal Coalition often causes instability and frequent sprains, balance training is critical:
- Single-leg stance exercises (progressing from stable to unstable surfaces).
- Wobble board training to improve ankle proprioception.
- Dynamic balance drills for athletes.
5. Gait Training
- Correcting abnormal walking patterns caused by stiffness and pain.
- Using orthotics or supportive footwear to optimize biomechanics.
6. Manual Therapy
- Gentle joint mobilization techniques to maximize available range of motion.
- Soft tissue release to reduce muscle tightness in surrounding structures.
7. Return-to-Sport Programs
For athletes, progressive functional training helps restore confidence:
- Plyometric drills (once pain-free).
- Agility ladders and sport-specific drills.
- Gradual return to high-impact activities.
At DMPhysios, the physiotherapy team ensures a structured progression — beginning with pain management and mobility work, then advancing to strengthening, balance, and return-to-sport rehabilitation. This patient-centered approach helps individuals avoid recurrence of pain and improves long-term outcomes.
Prevention
While congenital cases of Tarsal Coalition cannot be completely prevented, early intervention can reduce the risk of complications. Preventive strategies include:
- Regular foot assessments in children with flatfoot or family history.
- Wearing supportive footwear to reduce strain on the foot.
- Maintaining flexibility through stretching and mobility drills.
- Strength training for foot and ankle stability.
- Early physiotherapy intervention if stiffness, pain, or repeated sprains develop.
Parents should be especially alert if their child complains of foot pain, stiffness, or recurrent ankle sprains, as early detection allows for better management.
Conclusion
Tarsal Coalition is a condition that can significantly impact foot function, mobility, and overall quality of life if left untreated. With proper diagnosis, conservative treatment, and structured physiotherapy, individuals can regain control over their symptoms and lead active, pain-free lives.
At DMPhysios, a leading clinic in Noida specializing in spine and sports conditions, our focus is always on patient-centered rehabilitation. We provide comprehensive assessments and tailored physiotherapy treatment plans for Tarsal Coalition, ensuring patients not only recover but also prevent recurrence.If you or your child is struggling with persistent foot pain, stiffness, or recurrent ankle sprains, don’t ignore the signs. Early management can make all the difference. Book a consultation with DMPhysios today and take the first step toward pain-free, active living.