Overview
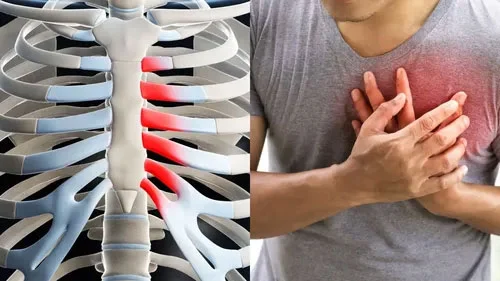
Tietze’s Syndrome is an uncommon yet benign musculoskeletal condition that primarily affects the costal cartilages of the chest wall. It is characterized by a painful, localized swelling where the upper ribs — most often the second or third — meet the sternum. This inflammation and thickening of the cartilage create a firm, tender lump that patients can often feel or see. A key distinction between Tietze’s Syndrome and the more frequently encountered costochondritis lies in the presence of this visible swelling; while both cause chest wall discomfort, costochondritis typically presents with pain alone, without any noticeable enlargement of the cartilage.
Because the chest pain associated with Tietze’s Syndrome can be sharp, aching, or radiating, it often resembles the discomfort caused by heart or lung disorders. This similarity can lead to confusion, unnecessary medical investigations, and heightened anxiety in affected individuals. Though the condition is not life-threatening and does not result in long-term damage to the heart or lungs, the recurrent episodes of pain and chest wall tenderness can disrupt daily life, limit physical activity, and impact emotional well-being.
A deeper understanding of Tietze’s Syndrome is therefore crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective symptom relief, and patient reassurance. Specialized clinics that focus on musculoskeletal, spine, and sports-related conditions — such as DMPhysios in Noida — are particularly well equipped to provide comprehensive care. Through a patient-centered approach, they not only address immediate symptoms but also focus on restoring functional mobility, improving posture, and preventing recurrences, ensuring individuals are able to return to normal living with confidence.
Symptoms
The hallmark symptom of Tietze’s Syndrome is localized chest pain with swelling at the costochondral junction. Symptoms may vary in severity and duration, but the most commonly reported include:
- Localized chest pain: Usually sharp or aching, often aggravated by deep breathing, coughing, sneezing, or physical exertion.
- Swelling: Noticeable, firm swelling at the affected rib-sternum joint, typically unilateral.
- Tenderness: Increased sensitivity upon palpation of the inflamed cartilage.
- Pain radiation: In some cases, pain may radiate to the shoulder, neck, or arm, mimicking cardiac or respiratory issues.
- Fluctuating intensity: Pain may come and go, lasting for weeks to months.
Unlike heart-related chest pain, Tietze’s Syndrome pain is usually localized, reproducible on palpation, and often linked to musculoskeletal activity.
Types of Tietze’s Syndrome
While there are no formal subtypes, Tietze’s Syndrome can be clinically categorized based on severity and duration:
- Acute Tietze’s Syndrome
- Sudden onset of pain and swelling.
- Usually triggered by trauma, coughing, or strain.
- Chronic/Recurrent Tietze’s Syndrome
- Long-standing condition with intermittent flare-ups.
- Pain may become less severe over time, but swelling persists.
This clinical distinction helps physiotherapists at DMPhysios design individualized rehabilitation programs tailored to patient needs.
Causes
The exact cause of Tietze’s Syndrome remains unclear, but several contributing factors have been identified:
- Repetitive strain or microtrauma – Activities involving repeated upper body exertion (e.g., lifting, pushing, or sports) can stress the costal cartilage.
- Respiratory infections or chronic coughing – Excessive coughing increases pressure on the rib cartilage, leading to inflammation.
- Chest trauma – Even minor injuries to the chest wall can trigger the condition.
- Post-surgical changes – Procedures involving the chest may irritate the cartilage.
- Idiopathic onset – In some patients, no identifiable cause is found.
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are more susceptible to developing Tietze’s Syndrome, including:
- Young adults (20–40 years old) – The condition is most common in this age group.
- Athletes – Sports that involve repetitive upper body strain, such as weightlifting, swimming, or rowing, increase the risk.
- Chronic cough sufferers – Individuals with asthma, bronchitis, or smokers may experience repeated strain on rib cartilage.
- Post-surgical patients – Thoracic surgery or sternotomy can predispose to inflammation.
- Poor posture and biomechanics – Excessive chest wall strain due to faulty posture may also contribute.
Recognizing these risk factors is essential for both prevention and long-term management, a key focus at DMPhysios, Noida’s leading spine and sports rehab clinic.
Treatment
Management of Tietze’s Syndrome usually involves conservative measures, as the condition is self-limiting in many cases. The primary treatment approaches include:
- Rest and activity modification – Avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms.
- Pain management – Over-the-counter medications such as NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen) help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Cold and heat therapy – Applying ice packs during acute flare-ups or heat pads for muscle relaxation.
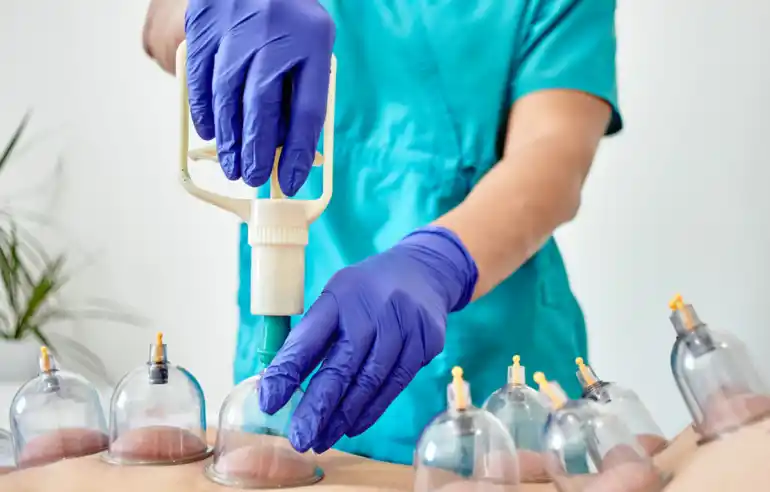
- Injections – In severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered to reduce inflammation.
- Reassurance and education – Explaining the benign nature of the condition to reduce patient anxiety about chest pain.
However, while medical management provides symptomatic relief, physiotherapy ensures long-term recovery and prevention of recurrences.
Physiotherapy Treatment
At DMPhysios in Noida, physiotherapy is central to the holistic management of Tietze’s Syndrome. A patient-centered rehabilitation approach addresses not only symptom relief but also underlying biomechanical issues.
1. Pain Relief Techniques
- Ultrasound therapy: Helps reduce deep tissue inflammation.
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): Provides effective pain modulation.
- Manual therapy: Gentle mobilization of the thoracic spine and rib cage improves movement and reduces stiffness.
2. Posture Correction
- Ergonomic training for sitting, standing, and work-related activities.
- Strengthening of postural muscles (upper back, scapular stabilizers) to reduce chest wall strain.
3. Breathing Exercises
- Diaphragmatic breathing reduces stress on chest wall muscles.
- Thoracic expansion exercises restore mobility and ease respiratory discomfort.
4. Stretching and Mobility
- Stretching of pectoral muscles, intercostals, and thoracic spine improves chest mobility.
- Rib mobilization techniques assist in restoring normal biomechanics.
5. Strengthening Exercises
- Gradual strengthening of shoulder girdle and upper back muscles.
- Core stabilization to support thoracic and rib cage function.
6. Patient Education and Lifestyle Guidance
- Teaching patients to avoid repetitive strain activities.
- Guidance on stress management and relaxation, as stress often worsens chest wall pain.
- Advice on proper breathing techniques during sports or workouts.
The physiotherapy team at DMPhysios ensures that each treatment plan is individualized, progressive, and evidence-based, helping patients return to daily activities without fear of recurrence.
Prevention
While not all cases can be prevented, adopting healthy lifestyle and postural habits reduces the risk:
- Maintain good posture – Especially while working on computers or lifting weights.
- Warm-up and stretching – Essential before sports or strenuous activities.
- Manage respiratory conditions – Early treatment of asthma, bronchitis, or chronic cough prevents chest wall strain.
- Avoid overtraining – Balance physical activity with adequate rest.
- Strengthen supporting muscles – Building endurance in postural and core muscles helps reduce stress on costal cartilages.
Preventive physiotherapy programs at DMPhysios often combine posture correction, ergonomic education, and exercise training to safeguard patients from recurrence.
Conclusion
Tietze’s Syndrome, though rare, can cause considerable distress due to chest pain and swelling that often mimics serious conditions like cardiac disorders. Early diagnosis, reassurance, and a multidisciplinary treatment approach are essential. While medications and rest can provide short-term relief, physiotherapy remains the cornerstone for long-term recovery, functional restoration, and prevention.
At DMPhysios in Noida, a clinic renowned for its expertise in spine and sports conditions, patients with Tietze’s Syndrome receive comprehensive, patient-centered rehabilitation. With a focus on pain relief, posture correction, breathing training, and strengthening, the physiotherapy team ensures that individuals regain confidence and return to their normal lifestyles.If you or someone you know is struggling with persistent chest pain and swelling that may be linked to Tietze’s Syndrome, don’t delay care. Reach out to DMPhysios, Noida’s trusted physiotherapy clinic, for expert evaluation and a personalized treatment plan designed for lasting relief.