Overview
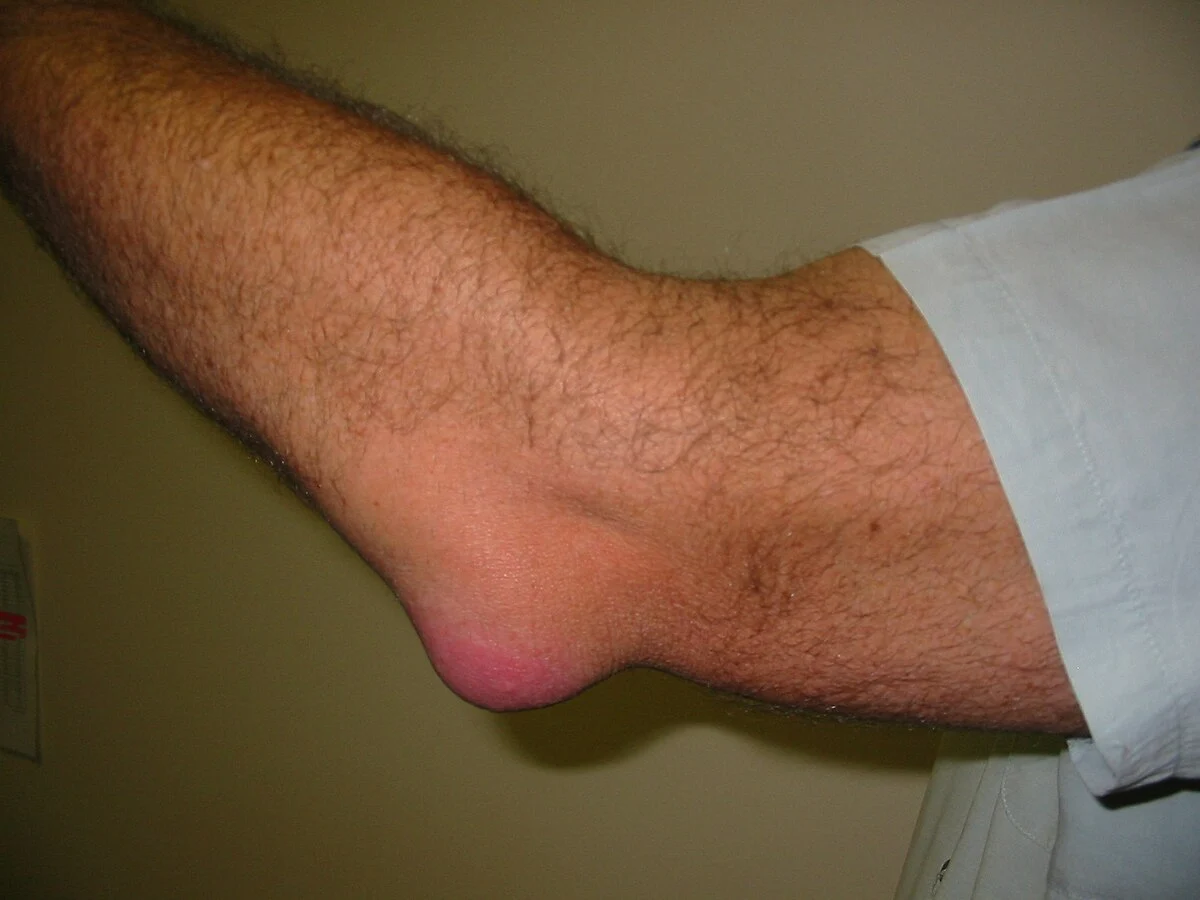
Olecranon bursitis, also commonly known as Student’s Elbow, is a painful inflammation of the olecranon bursa, a small fluid-filled sac located at the tip of the elbow. The function of this bursa is to reduce friction between the skin and the underlying bony prominence of the olecranon process (the pointed end of the ulna). When this bursa becomes irritated or inflamed due to repetitive trauma, pressure, or infection, it leads to olecranon bursitis.
The condition is often referred to as Student’s Elbow because it is frequently seen in individuals who rest their elbows on hard surfaces for prolonged periods—such as students, office workers, or people engaged in desk jobs.
At DMPhysios, a leading physiotherapy clinic in Noida specializing in spine and sports conditions, olecranon bursitis is a commonly treated upper limb issue. The clinic focuses on patient-centered rehabilitation, ensuring both pain relief and long-term functional restoration.
Symptoms
The presentation of olecranon bursitis can range from mild swelling to severe pain and restricted elbow motion. The following are the most common symptoms:
- Swelling at the tip of the elbow:
The hallmark sign is a noticeable, soft, and fluid-like swelling over the back of the elbow. This may develop gradually or suddenly. - Pain or tenderness:
Pain may be mild in chronic cases but can be sharp or throbbing if infection or trauma is involved. - Redness and warmth:
The skin over the affected area may appear red, shiny, and warm to the touch, particularly in cases of septic olecranon bursitis. - Restricted elbow movement:
Due to swelling and discomfort, patients often find it difficult to fully bend or extend the elbow. - Fluctuation in swelling size:
The swelling might increase after activity or pressure and reduce during rest. - Systemic symptoms (in infection):
Fever, chills, and fatigue may occur in septic cases, indicating that the infection has spread.
Types of Olecranon Bursitis
Olecranon bursitis can be categorized into two main types depending on the underlying cause:
1. Aseptic (Non-infectious) Olecranon Bursitis
This is the most common form. It occurs due to repetitive trauma, friction, or prolonged pressure on the elbow. It is often seen in students, plumbers, mechanics, and athletes who frequently lean on their elbows or engage in activities that stress the joint.
2. Septic (Infectious) Olecranon Bursitis
This occurs when bacteria, usually Staphylococcus aureus, enter the bursa through a small cut, wound, or puncture near the elbow. The area becomes red, hot, and painful, sometimes with pus accumulation. If untreated, it can lead to abscess formation or deeper joint infections.
Causes
There are several factors that can lead to the inflammation of the olecranon bursa. Common causes include:
- Repetitive pressure or friction:
Constant leaning on hard surfaces (e.g., desks, floors) compresses the bursa and leads to irritation. - Direct trauma:
A sudden blow or fall on the elbow can cause bleeding into the bursa, resulting in inflammation. - Prolonged static posture:
Students, office workers, or drivers who rest their elbows for long periods are at higher risk. - Infection:
Cuts, abrasions, or insect bites near the elbow can allow bacteria to enter and infect the bursa. - Underlying medical conditions:
Disorders such as gout, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes mellitus increase the likelihood of olecranon bursitis. - Previous elbow surgery:
Post-surgical irritation or altered joint biomechanics can also lead to bursitis.
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are more prone to developing olecranon bursitis due to their lifestyle, occupation, or medical background. These include:
- Students, clerks, and IT professionals
- Manual laborers (plumbers, mechanics, electricians)
- Athletes (wrestlers, weightlifters, and cricket players)
- People with inflammatory joint diseases
- Individuals with weakened immune systems
- Those with repetitive stress or microtrauma to the elbow
At DMPhysios in Noida, the physiotherapy experts carefully assess these risk factors to customize treatment programs that address not just the symptoms but also the underlying causes.
Treatment
The management of olecranon bursitis depends on the cause, severity, and presence or absence of infection. The main goals are to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, prevent recurrence, and restore normal elbow function.
1. Conservative Treatment
In mild to moderate aseptic cases, conservative management is effective and includes:
- Rest and activity modification:
Avoiding leaning or applying pressure on the affected elbow helps reduce irritation. - Ice therapy:
Applying ice packs several times a day can help reduce pain and swelling. - Compression:
Using an elastic bandage or compression sleeve can help limit fluid accumulation. - Elevation:
Keeping the elbow elevated above heart level assists in reducing swelling. - Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs):
Medications like ibuprofen or diclofenac help control pain and inflammation.
2. Aspiration
If swelling is significant, a physician may aspirate (drain) the accumulated fluid using a sterile needle. This procedure also allows the fluid to be tested for infection.
3. Antibiotics (for Septic Bursitis)
If infection is confirmed, appropriate antibiotics are prescribed. In severe or chronic septic cases, surgical drainage or bursectomy (removal of the bursa) may be necessary.
4. Surgical Management
Surgery is reserved for persistent, recurrent, or infected olecranon bursitis that does not respond to conservative measures. Post-surgery, physiotherapy becomes crucial for restoring elbow movement and preventing stiffness.
Physiotherapy Treatment
At DMPhysios, a renowned physiotherapy clinic in Noida specializing in spine and sports conditions, patient-centered rehabilitation is the core philosophy. Physiotherapists at DMPhysios adopt a structured, evidence-based approach for olecranon bursitis rehabilitation, focusing on pain control, functional recovery, and long-term prevention.
Phase 1: Pain and Inflammation Control
Goals: Reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.
Interventions:
- Cryotherapy (Ice therapy): 10–15 minutes, 3–4 times a day to minimize swelling.
- Accelerated Healing Therapy: Helps promote healing and reduces inflammation.
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): For pain relief.
- Elbow padding: To protect the bursa and reduce pressure during daily activities.
- Activity modification: Avoid prolonged leaning or repetitive movements.
Phase 2: Restoring Range of Motion
Goals: Gradually regain elbow mobility without aggravating symptoms.
Interventions:
- Gentle active and passive range of motion exercises:
Flexion, extension, pronation, and supination movements performed in a pain-free range. - Stretching of surrounding muscles: Especially triceps and forearm extensors to prevent stiffness.
- Soft tissue mobilization: Helps reduce adhesions and improve circulation.
Phase 3: Strengthening and Functional Restoration
Goals: Improve muscle strength and stability around the elbow.
Interventions:
- Isometric exercises: Early strengthening without joint movement to maintain muscle tone.
- Progressive resistance exercises: Using light weights or resistance bands to strengthen triceps, biceps, and forearm muscles.
- Proprioceptive training: Enhances joint stability and control.
- Functional training: Reintroduce work-related or sports-specific activities gradually.
Phase 4: Prevention and Maintenance
Goals: Prevent recurrence and maintain optimal elbow health.
Interventions:
- Ergonomic correction: Educating patients on proper desk or work setup.
- Elbow protectors or cushions: Especially for individuals whose occupations involve elbow support on hard surfaces.
- Home exercise program: Stretching and strengthening routines to be continued regularly.
- Postural correction: Addressing shoulder and neck alignment to reduce stress on the upper limb.
At DMPhysios, the physiotherapy team integrates manual therapy, electrotherapy, and exercise rehabilitation to ensure complete recovery. They also emphasize education and lifestyle modification, empowering patients to avoid recurrence.
Prevention
Prevention plays a vital role, especially for those who have recurring episodes. The following steps can minimize the risk of olecranon bursitis:
- Avoid leaning on elbows for long durations.
- Use soft cushioning or elbow pads when studying or working at desks.
- Maintain good posture during office or computer work.
- Perform regular stretching of triceps and forearm muscles.
- Treat minor cuts or abrasions promptly to prevent infection.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet to support joint and soft tissue health.
- Seek physiotherapy early at clinics like DMPhysios in Noida, where experts can detect and address early inflammation before it worsens.
Conclusion
Olecranon bursitis (Student’s Elbow), though often considered minor, can significantly affect daily activities if not managed appropriately. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for early intervention and full recovery.
At DMPhysios, a trusted physiotherapy clinic in Noida specializing in spine and sports conditions, patients receive patient-centered rehabilitation designed to relieve pain, restore function, and prevent recurrence. Their expert physiotherapists use a combination of manual therapy, exercise prescription, and ergonomic education to ensure long-term relief from olecranon bursitis.
If you’re struggling with elbow swelling, pain, or restricted movement, don’t wait for it to worsen.
Visit DMPhysios today, where expert care, advanced treatment, and individualized attention come together to help you heal better, move better, and live pain-free.