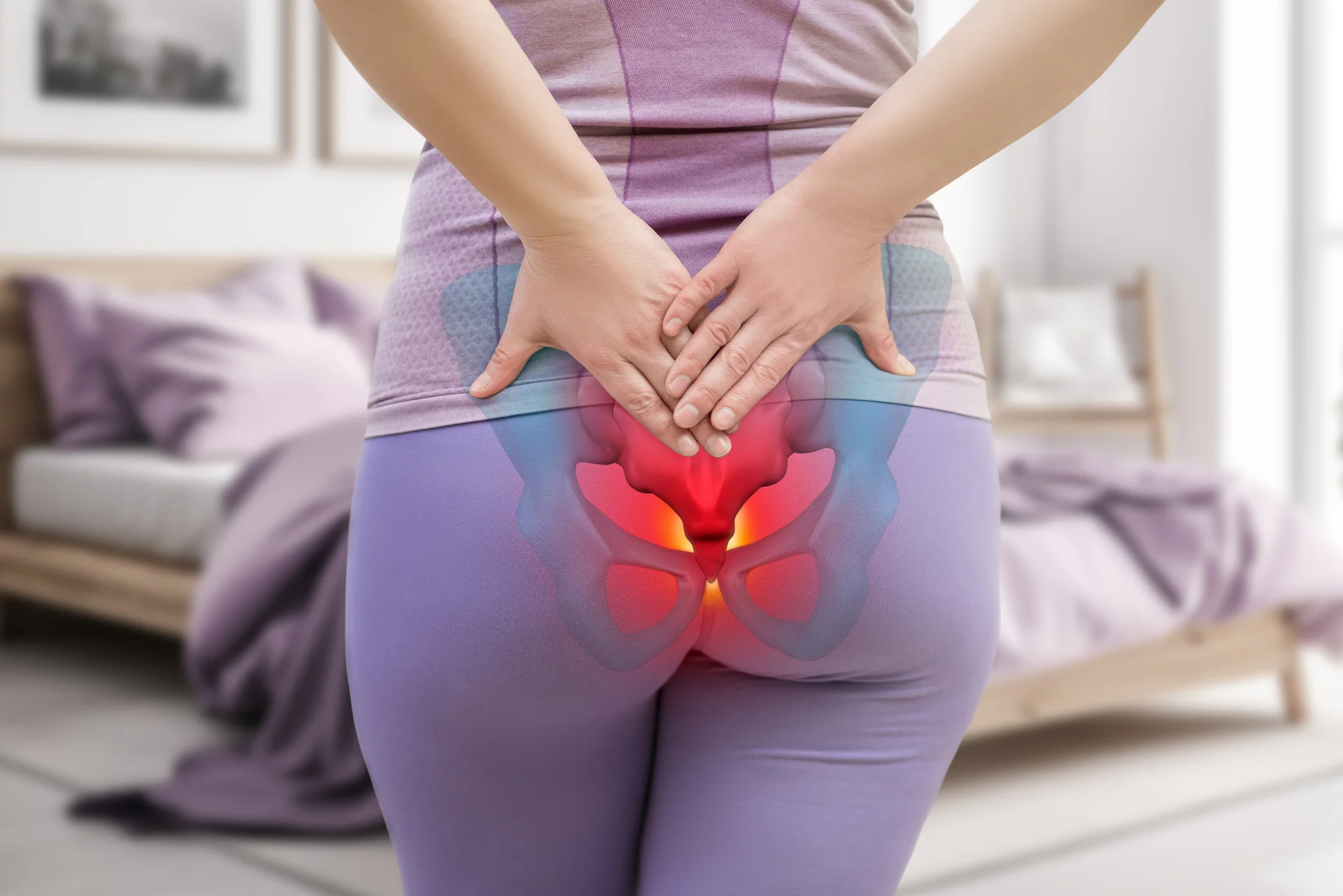
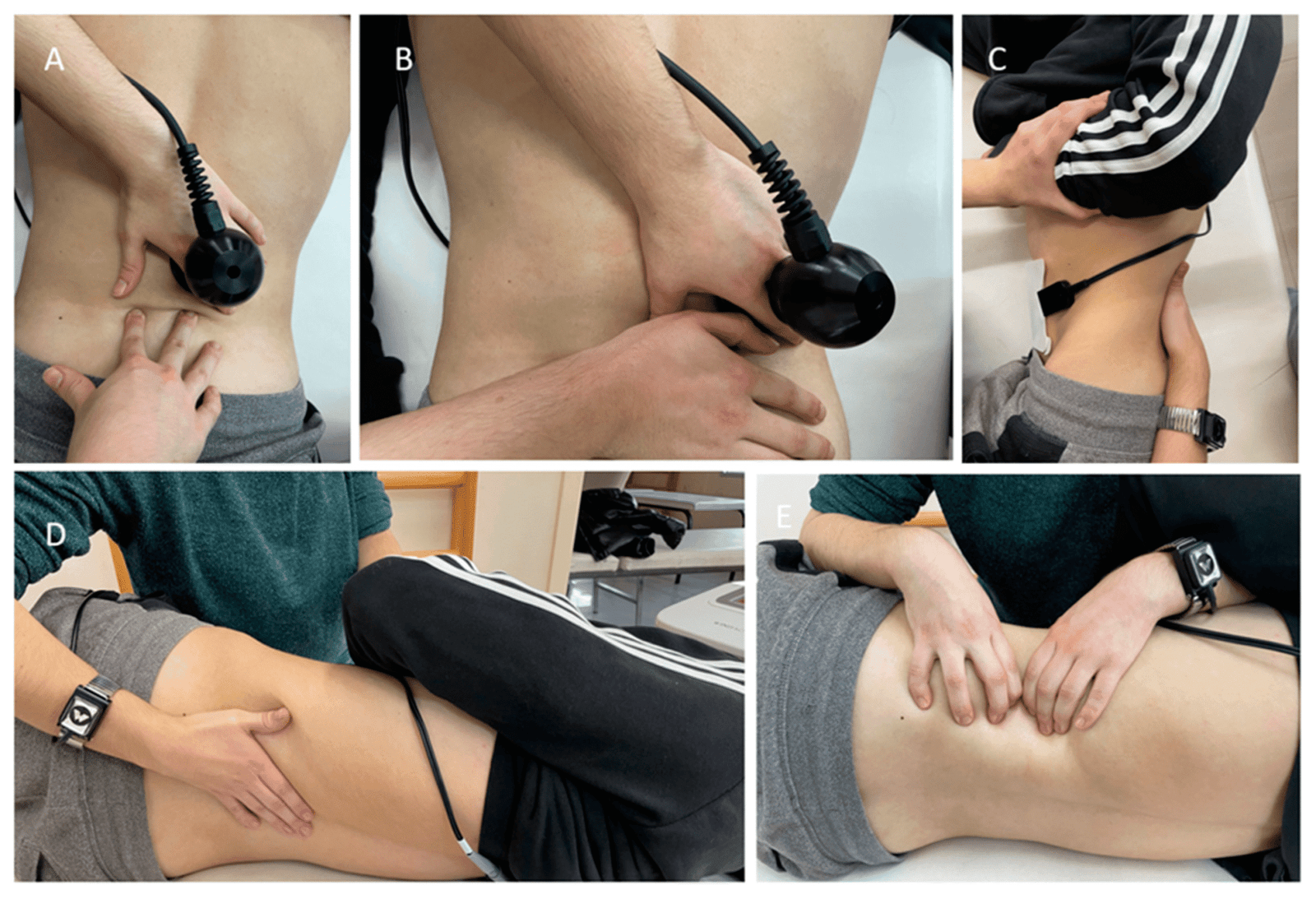
Coccydynia, commonly known as tailbone pain, involves discomfort at the base of the spine, specifically in the coccyx region.
Diseases & Conditions
Easy-to-understand answers about diseases and conditions
Find diseases & conditions by first letter
Overview
Coccydynia, commonly known as tailbone pain, involves discomfort at the base of the spine, specifically in the coccyx region. This condition can result from various factors, including trauma, prolonged sitting on hard surfaces, or repetitive pressure on the tailbone.
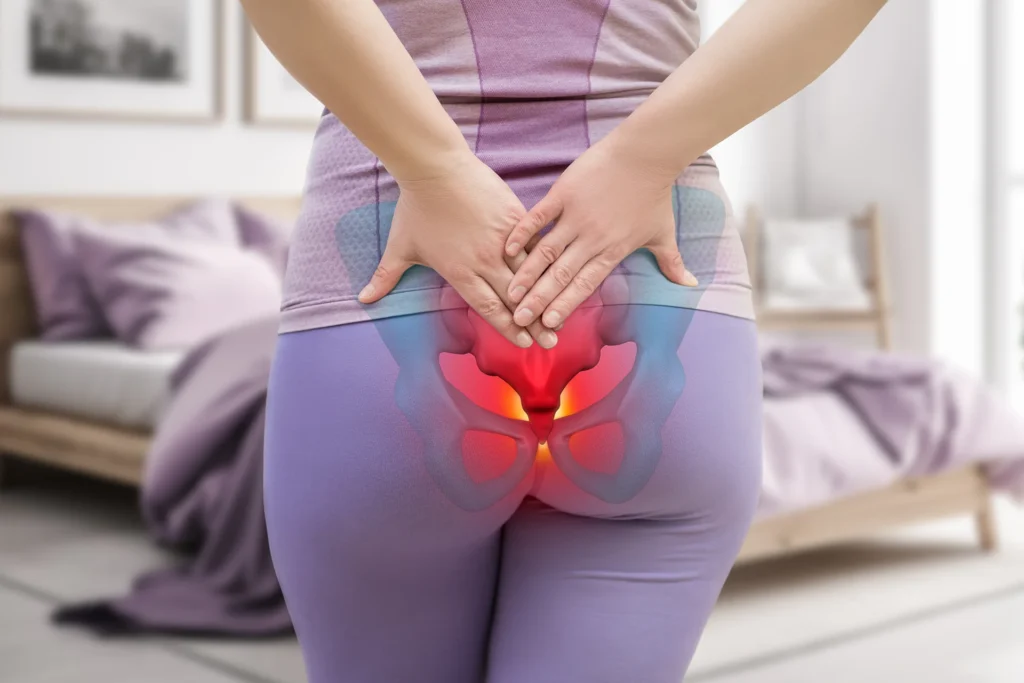

Symptoms
- Localized pain at the tailbone, especially when sitting or transitioning from sitting to standing.
- Tenderness around coccyx
- Pain worsening with activities like cycling, prolonged sitting, or bowel movements.
- Occasional numbness or tingling in the surrounding area (less common).
Causes
- Trauma: A direct impact on the tailbone, such as falling onto it, or sustained pressure from sitting on hard surfaces for extended periods.
- Childbirth: The pressure during delivery can sometimes injure or strain the coccyx.
- Poor Posture: Slouching or improper sitting positions increase pressure on the tailbone.
- Degenerative Joint Changes: Age related or Arthritis or wear-and-tear changes in the coccyx region.
- Infections or Tumors: infections or tumors of coccyx may cause pain.
Treatments
Physiotherapy is a key treatment option for managing and relieving coccydynia.
1. Assessment and Diagnosis
A physiotherapist will evaluate your posture, movement patterns, and coccyx mobility to identify contributing factors.
2. Pain Management
Techniques like manual therapy, soft tissue massage, and gentle mobilization can reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
3. Postural Education
Learning proper sitting posture and ergonomics can significantly reduce pressure on the tailbone. Physiotherapists often recommend using cushions designed to offload the coccyx.
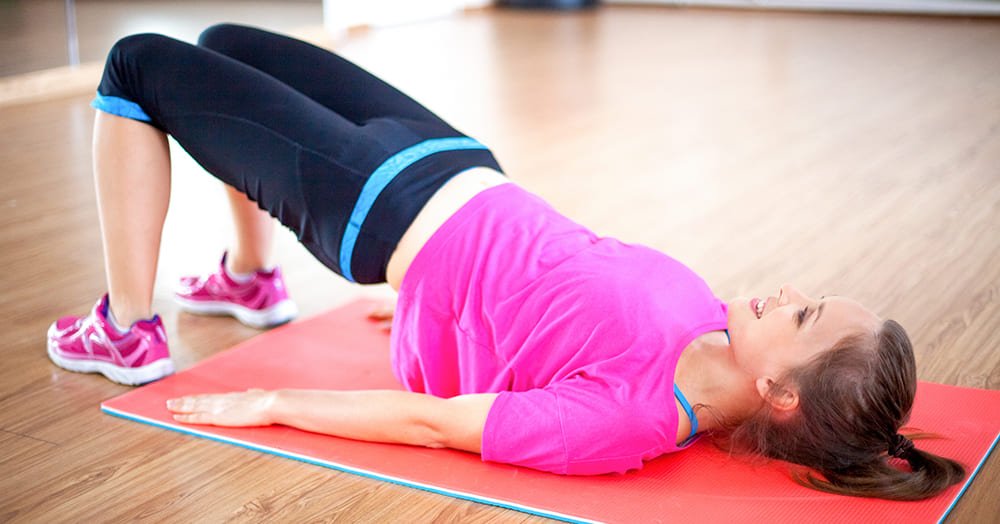
4. Exercise Therapy
Targeted exercises to strengthen pelvic floor muscles, improve core stability, and enhance flexibility can promote healing and prevent recurrence.
5. Activity Modification
Guidance on modifying daily activities and avoiding triggers helps in managing pain during the recovery process.
Other Disease
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo
Feel Free to ask us
Patient-centered care
Patient-centred care is about treating a person receiving healthcare with dignity and respect and involving them in all decisions about their health. This type of care is also called ‘person-centred care’. It is an approach that is linked to a person’s healthcare rights.
Family-friendly environment
Aside from the treatment program, an overlooked aspect of treatment is the environment. Many people do not realize how big a factor this is for those who want to recover.
Supportive peer mentorship community
Mentorship and peer support are pivotal in creating environments that nurture personal and collective growth, learning, and success, making each feel connected and valued.
Coccydynia: Causes, Symptoms, and Physiotherapy Treatments
What is Coccydynia?
C occydynia, commonly known as tailbone pain, involves discomfort at the base of the spine, specifically in the coccyx region. This condition can result from various factors, including trauma, prolonged sitting on hard surfaces, or repetitive pressure on the tailbone.
Causes of Coccydynia
Trauma: A direct impact on the tailbone, such as falling onto it, or sustained pressure from sitting on hard surfaces for extended periods.
Childbirth: The pressure during delivery can sometimes injure or strain the coccyx.
Poor Posture: Slouching or improper sitting positions increase pressure on the tailbone.
Degenerative Joint Changes: Age related or Arthritis or wear-and-tear changes in the coccyx region.
Infections or Tumors: infections or tumors of coccyx may cause pain.
Symptoms
Localized pain at the tailbone, especially when sitting or transitioning from sitting to standing.
Tenderness around coccyx
Pain worsening with activities like cycling, prolonged sitting, or bowel movements.
Occasional numbness or tingling in the surrounding area (less common).
How Can Physiotherapy Help?
Physiotherapy is a key treatment option for managing and relieving coccydynia.
1. Assessment and Diagnosis
A physiotherapist will evaluate your posture, movement patterns, and coccyx mobility to identify contributing factors.
2. Pain Management
Techniques like manual therapy, soft tissue massage, and gentle mobilization can reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
3. Postural Education
Learning proper sitting posture and ergonomics can significantly reduce pressure on the tailbone. Physiotherapists often recommend using cushions designed to offload the coccyx.
4. Exercise Therapy
Targeted exercises to strengthen pelvic floor muscles, improve core stability, and enhance flexibility can promote healing and prevent recurrence.
5. Activity Modification
Guidance on modifying daily activities and avoiding triggers helps in managing pain during the recovery process.