Overview
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic, progressive inflammatory disorder that predominantly targets the spine and sacroiliac joints—the joints where the spine meets the pelvis. Characterized by persistent pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, Ankylosing Spondylitis belongs to a broader group of conditions known as axial spondyloarthritis.
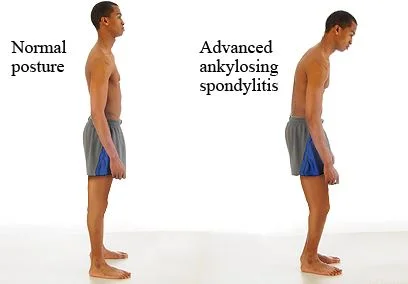
What makes this condition particularly concerning is its long-term impact: ongoing inflammation can eventually cause sections of the spinal vertebrae to fuse together—a process called ankylosis—leading to a loss of flexibility and, in some cases, a permanently stooped posture. This fusion not only restricts movement but can also interfere with lung function when the ribcage becomes involved, thereby compromising overall quality of life.
Ankylosing Spondylitis typically emerges in early adulthood, most commonly between the ages of 17 and 45, though it can occasionally present earlier or later. Unfortunately, because early symptoms often resemble those of mechanical or postural back pain, the condition can remain undiagnosed for years, leading to unnecessary progression and joint damage. This diagnostic delay highlights the importance of professional awareness and timely referral.
At DMPhysios, a specialized spine and sports rehabilitation clinic based in Noida, we recognize the subtle signs of Ankylosing Spondylitis early on. Through clinical screening, advanced physical assessments, and collaborative care, we prioritize early detection and evidence-based interventions. Our goal is not only to preserve spinal mobility but also to enhance long-term function, independence, and quality of life for every individual under our care.
Symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Recognizing the symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis is crucial for timely intervention. Although symptoms may differ among individuals, typical indicators include:
- Ongoing lower back pain and stiffness, particularly noticeable in the morning or after long periods of inactivity.
- Discomfort tends to ease with physical activity but not with rest.
- Limited spinal mobility due to inflammation or fusion.
- Fatigue, a common feature of chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Discomfort may also occur in other joints, including the hips, shoulders, or knees.
- Enthesitis, or inflammation where ligaments and tendons attach to bone (e.g., Achilles tendon).
- Uveitis, an inflammation of the eye, is a common extra-articular manifestation.
- In severe cases, a forward-stooped posture may develop.
At DMPhysios in Noida, our multidisciplinary approach ensures that even non-spinal symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis are not overlooked in the treatment process.
Types of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Although Ankylosing Spondylitis is recognized as a distinct clinical entity within the spondyloarthritis spectrum, its presentation can vary significantly depending on the stage of progression and the visibility of structural changes on imaging studies. Understanding the types of Ankylosing Spondylitis is crucial for timely diagnosis, effective treatment planning, and accurate prognosis.
1. Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA)
- This form represents the early or less structurally advanced stage of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis experience classic clinical symptoms—such as chronic back pain, morning stiffness, and fatigue—but without any definitive changes visible on traditional X-rays of the spine or sacroiliac joints. However, more sensitive imaging techniques like MRI may reveal inflammation in the sacroiliac region or other soft tissue changes suggestive of early disease activity.
- This subtype is particularly important to recognize because it is often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed as mechanical back pain. Early intervention during this phase can prevent structural damage and long-term disability. At DMPhysios, we use thorough clinical screening and advanced diagnostic collaboration to identify non-radiographic cases early, ensuring that patients receive targeted physiotherapy and medical management before irreversible changes occur.
2. Radiographic Ankylosing Spondylitis (r-axSpA)
- Radiographic AS represents the more advanced and structurally defined stage of the condition. In this form, visible changes in the sacroiliac joints or spine can be seen on standard X-rays. These changes often include erosions, sclerosis, joint space narrowing, and in severe cases, bony fusion (ankylosis) of the vertebrae. Patients with radiographic AS typically have a longer disease history and may present with significant spinal stiffness, altered posture, and reduced functional capacity.
Identifying the stage and subtype of Ankylosing Spondylitis helps our experts at DMPhysios to tailor rehabilitation plans that match the patient’s individual condition and needs.
Causes of Ankylosing Spondylitis
The exact cause of Ankylosing Spondylitis remains unknown, but research points towards a strong genetic component.
- HLA-B27 gene: The presence of this gene is found in over 90% of individuals with Ankylosing Spondylitis, although not everyone who carries the gene develops the condition.
- Immune dysregulation: The immune system erroneously attacks the body’s own tissues, especially the spinal joints.
- Environmental triggers: Infections or gut imbalances may act as catalysts in genetically predisposed individuals.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing Ankylosing Spondylitis:
- Genetics: Family history is the strongest predictor.
- Gender: The condition tends to affect males more frequently than females.
- Age: Most often begins in late adolescence or early adulthood.
- HLA-B27 gene: As mentioned earlier, this gene significantly raises risk.
- Autoimmune diseases: Individuals with a history of other autoimmune or inflammatory conditions may be more prone.
At DMPhysios, genetic screening, medical history, and advanced assessment tools help us detect risk early and begin management before irreversible damage occurs.
Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis focuses on:
1. Medication
- NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): First-line treatment to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs): Such as sulfasalazine, especially when peripheral joints are involved.
- Biologics (TNF-alpha and IL-17 inhibitors): Used in moderate-to-severe cases unresponsive to NSAIDs.
- Corticosteroid injections: For targeted pain relief in severe joint inflammation.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
- Regular low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, and yoga.
- Avoiding prolonged inactivity.
- Practicing posture correction exercises.
3. Surgical Intervention
Surgery is rare but may be considered for severe hip involvement or spinal deformity.
Physiotherapy Treatment for Ankylosing Spondylitis at DMPhysios
At DMPhysios, Noida, we specialize in patient-centered rehabilitation for Ankylosing Spondylitis. Our philosophy combines clinical expertise with personalized care. Here’s how we treat AS patients through physiotherapy:
1. Pain Relief & Inflammation Control
- Accelerated Healing Therapy: Advanced Electrotherapy for reducing inflammation in the sacroiliac joints or lumbar spine.
- Manual Therapy: Gentle mobilization of the thoracic spine, SI joints, and hips to relieve stiffness.
2. Postural Training
- We emphasize postural awareness and retraining, especially in early stages of spinal rigidity.
- Mirror feedback, posture correction drills, and scapular stabilization exercises are part of our regular sessions.
3. Flexibility & Mobility Programs
- A customized stretching routine for the spine, hip flexors, hamstrings, and chest muscles is implemented.
- Breathing exercises and thoracic expansion drills prevent ribcage stiffness, improving lung capacity.
4. Strengthening Exercises
- Core muscle strengthening is key to spinal stability.
- Isometric and dynamic strengthening of the glutes, back extensors, and deep abdominal muscles help reduce compensatory pain.
5. Aquatic Therapy
- Offered in select cases, water exercises reduce joint loading while promoting full-range movements.
6. Home Exercise Program
- Patients receive a structured home plan with progressions based on their tolerance and mobility level.
- Education on ergonomics and sleep posture is also provided.
At DMPhysios, our team of certified physiotherapists takes pride in tracking your progress through regular assessments and digital records, ensuring each Ankylosing Spondylitis patient receives the most up-to-date care.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
Although Ankylosing Spondylitis cannot be cured, its progression can be slowed, and symptoms managed effectively with a proactive approach:
- Regular physical activity is the cornerstone.
- Avoid smoking, which accelerates spinal damage.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on joints.
- Routine physiotherapy check-ins at centers like DMPhysios can help in maintaining alignment and avoiding flare-ups.
Early diagnosis and consistent physiotherapy play a vital role in maintaining independence and minimizing long-term disability.
Conclusion: Empowering Patients at DMPhysios
Ankylosing Spondylitis is more than just back pain—it’s a lifelong condition that demands awareness, consistent effort, and professional support. At DMPhysios, we are committed to helping patients reclaim control over their lives through science-backed, personalized, and holistic rehabilitation.
Whether you are recently diagnosed or have been living with Ankylosing Spondylitis for years, our team in Noida is ready to guide you with care that adapts to your lifestyle, pace, and goals.
Don’t wait for stiffness to become a setback.
Book your consultation with DMPhysios today and let us help you stay strong, mobile, and pain-free.Visit us at DMPhysios – Noida’s leading clinic for Spine and Sports Rehab, where patient-centered care is our top priority.