Overview
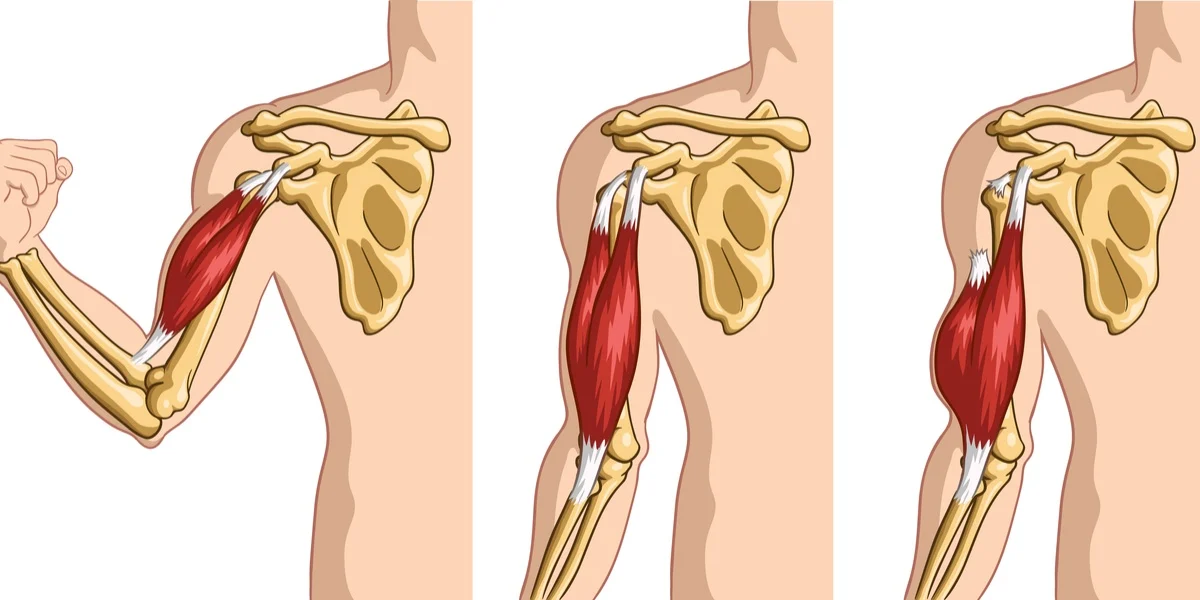
The biceps muscle, positioned prominently at the front of the upper arm, is one of the most important muscles for upper limb function. It assists in two key movements — elbow flexion, which allows you to bend your arm, and forearm supination, which enables you to rotate your forearm outward, such as when turning a doorknob or lifting a glass. This muscle connects to the skeleton through two main points at the shoulder (known as the proximal tendons — the long head and the short head) and one at the elbow (the distal tendon). These tendons are strong, fibrous structures that transmit the power generated by the biceps muscle to the bones of the shoulder and forearm.
When any of these tendons is overstressed or weakened and then tears — whether partially or completely — the injury is referred to as a biceps tendon rupture. This condition disrupts the normal function of the upper limb and may significantly impact day-to-day activities, especially those requiring lifting, carrying, or rotation of the forearm.
A biceps tendon rupture often presents with sudden pain, an audible “pop” or snapping sensation, and an immediate decrease in arm strength or endurance. While it can occur in anyone, it is especially common among athletes engaged in repetitive upper limb activities, manual workers who perform heavy lifting, and older adults whose tendons have undergone age-related degeneration.
At DMPhysios, a premier clinic in Noida specializing in spine and sports-related conditions with a strong focus on patient-centered rehabilitation, individuals experiencing a biceps tendon rupture receive thorough clinical evaluation, state-of-the-art diagnostics, and evidence-based physiotherapy interventions. This comprehensive approach is designed to not only restore the lost strength, movement, and function of the arm but also to educate and empower patients to prevent recurrence and safely return to their active lifestyles.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a biceps tendon rupture vary depending on whether the tear occurs at the shoulder (proximal) or elbow (distal), and whether it is partial or complete. Common signs include:
- Sudden, sharp pain in the upper arm or elbow at the time of injury.
- A popping or snapping sensation when the tendon tears.
- Visible deformity, often described as the “Popeye sign,” where the biceps muscle bulges because it retracts after the tendon tears.
- Bruising or discoloration around the upper arm or elbow within hours or days.
- Weakness in elbow flexion or forearm rotation (supination).
- Tenderness and swelling over the affected area.
Early recognition of these symptoms is critical. At DMPhysios, clinicians perform detailed physical assessments and functional tests to confirm whether a biceps tendon rupture is partial or complete, and to decide on the best course of management.
Types of Biceps Tendon Rupture
Understanding the type of biceps tendon rupture is essential for treatment planning. There are two main classifications:
1. Proximal Biceps Tendon Rupture
This involves the long head of the biceps at the shoulder joint. It is more common, particularly in older adults with degenerative tendon changes. Despite the rupture, some function of the biceps is usually retained because the short head tendon remains intact.
2. Distal Biceps Tendon Rupture
This occurs at the elbow where the tendon attaches to the radial tuberosity. Though less common, it is more serious because the single distal tendon is the only attachment at the elbow. Without prompt treatment, patients can lose significant strength in elbow flexion and supination.
3. Partial vs. Complete Rupture
A partial rupture means only some tendon fibers have torn, whereas a complete rupture indicates the tendon has fully detached. Partial tears may progress if not treated, so timely evaluation at a facility like DMPhysios is recommended.
Causes
A biceps tendon rupture can result from either acute injury or chronic degeneration:
- Sudden overload: Lifting a heavy object or forcefully extending the arm against resistance.
- Repetitive overhead activities: Athletes such as cricketers, weightlifters, and swimmers place repeated stress on the biceps tendon.
- Degenerative changes: Age-related wear and tear weakens the tendon, making it more prone to rupture.
- Trauma: Falls on an outstretched arm or direct impact to the shoulder or elbow.
- Steroid use: Chronic use of corticosteroids may weaken tendons over time.
At DMPhysios, the team emphasizes not only treating the injury but also identifying underlying movement or load factors that predispose someone to a biceps tendon rupture.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of a biceps tendon rupture:
- Age over 40: Tendons lose elasticity and strength.
- Male gender: Men are more frequently affected.
- Athletic or manual labor professions: Jobs or sports requiring heavy lifting or repetitive arm movements.
- Smoking: Reduces blood supply to tendons, impairing healing.
- Pre-existing shoulder or elbow conditions: Rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement, or previous tendonitis can predispose to rupture.
- Corticosteroid injections into the tendon region: Can weaken the tendon over time.
Knowing these risk factors allows clinics like DMPhysios to design individualized prevention and rehabilitation strategies.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type, severity, and functional demands of the patient.
Non-Surgical Management
For many proximal biceps tendon ruptures, non-surgical management is sufficient, especially for older or less active individuals. This includes:
- Rest and activity modification.
- Ice and anti-inflammatory measures to reduce pain and swelling.
- Short-term use of a sling to support the arm.
- Gradual rehabilitation to restore motion and strength.
Surgical Repair
Distal biceps tendon ruptures or complete ruptures in active individuals usually require surgical reattachment of the tendon to restore function. Surgery is ideally performed within 2–3 weeks of injury to prevent tendon retraction. After surgery, physiotherapy plays a crucial role in recovery.
At DMPhysios, patients receive a clear explanation of both surgical and non-surgical options, empowering them to make informed choices.
Physiotherapy Treatment
Physiotherapy is central to restoring function after a biceps tendon rupture, whether managed conservatively or surgically. At DMPhysios, the approach is evidence-based and patient-centered.
1. Acute Phase (0–2 weeks)
Goals:
- Protect the healing tendon.
- Reduce pain and inflammation.
- Maintain mobility of adjacent joints.
Interventions:
- Cryotherapy or cold packs to minimize swelling.
- Gentle passive and pain-free active-assisted range-of-motion exercises for the shoulder, elbow, and wrist.
- Scapular stabilization exercises to maintain upper limb posture.
- Education on activity modification to avoid stressing the tendon.
2. Early Rehabilitation Phase (2–6 weeks)
Goals:
- Gradually restore range of motion.
- Begin light isometrics.
- Prevent stiffness and atrophy.
Interventions:
- Progress from passive to active range-of-motion of the elbow and forearm.
- Isometric contractions of the biceps and surrounding muscles within pain-free limits.
- Soft tissue mobilization around the shoulder and elbow to reduce adhesions.
- Postural correction and core activation to support functional arm movement.
3. Strengthening Phase (6–12 weeks)
Goals:
- Rebuild strength and endurance.
- Improve neuromuscular control.
- Restore functional patterns.
Interventions:
- Gradual introduction of resisted elbow flexion and supination using light weights or elastic bands.
- Progressive resistance training for the rotator cuff, scapular stabilizers, and forearm muscles.
- Closed-chain exercises such as wall push-ups to improve kinetic chain integration.
- Proprioceptive and coordination drills (e.g., ball catching, perturbations).
4. Advanced / Return-to-Sport Phase (3–6 months)
Goals:
- Restore full strength, power, and function.
- Prepare for occupational or sport-specific demands.
Interventions:
- High-level strengthening and endurance programs tailored to the patient’s goals.
- Plyometric or dynamic exercises for athletes.
- Sport-specific drills (e.g., throwing mechanics, lifting technique).
- Education on injury prevention and load management.
Throughout all phases, DMPhysios therapists monitor progress using objective measures like strength testing, functional scores, and pain scales. This ensures that each patient with a biceps tendon rupture progresses safely and confidently toward recovery.
Prevention
While not all biceps tendon ruptures can be prevented, certain strategies reduce risk:
- Regular strengthening: Focus on balanced training of the biceps, rotator cuff, and scapular stabilizers.
- Warm-up and stretching before sports or heavy lifting.
- Avoid sudden overload: Gradually increase training intensity and volume.
- Ergonomic adjustments at work to reduce repetitive strain.
- Quit smoking and adopt a healthy lifestyle to maintain tendon health.
- Early treatment of tendonitis: Address pain and inflammation promptly to prevent progression to rupture.
At DMPhysios, prevention is as important as treatment. The clinic offers screening programs, ergonomics counseling, and individualized exercise plans for athletes and workers at risk of biceps tendon rupture.
Conclusion
A biceps tendon rupture can be a life-disrupting injury, leading to pain, weakness, and loss of confidence in everyday tasks or sports performance. However, with prompt diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and structured rehabilitation, most people can regain excellent function.
At DMPhysios, a trusted clinic in Noida specializing in spine and sports conditions with patient-centered rehab, patients with biceps tendon rupture benefit from a multidisciplinary approach combining expert physiotherapy, education, and tailored exercise programs. Whether you are an athlete wanting to return to your sport or someone recovering from an unexpected injury, DMPhysios provides compassionate, evidence-based care to guide you every step of the way.
If you suspect you have a biceps tendon rupture or are struggling with arm pain and weakness, don’t wait—book an assessment at DMPhysios today. Our team will help you heal, rebuild strength, and prevent future injuries.