Overview
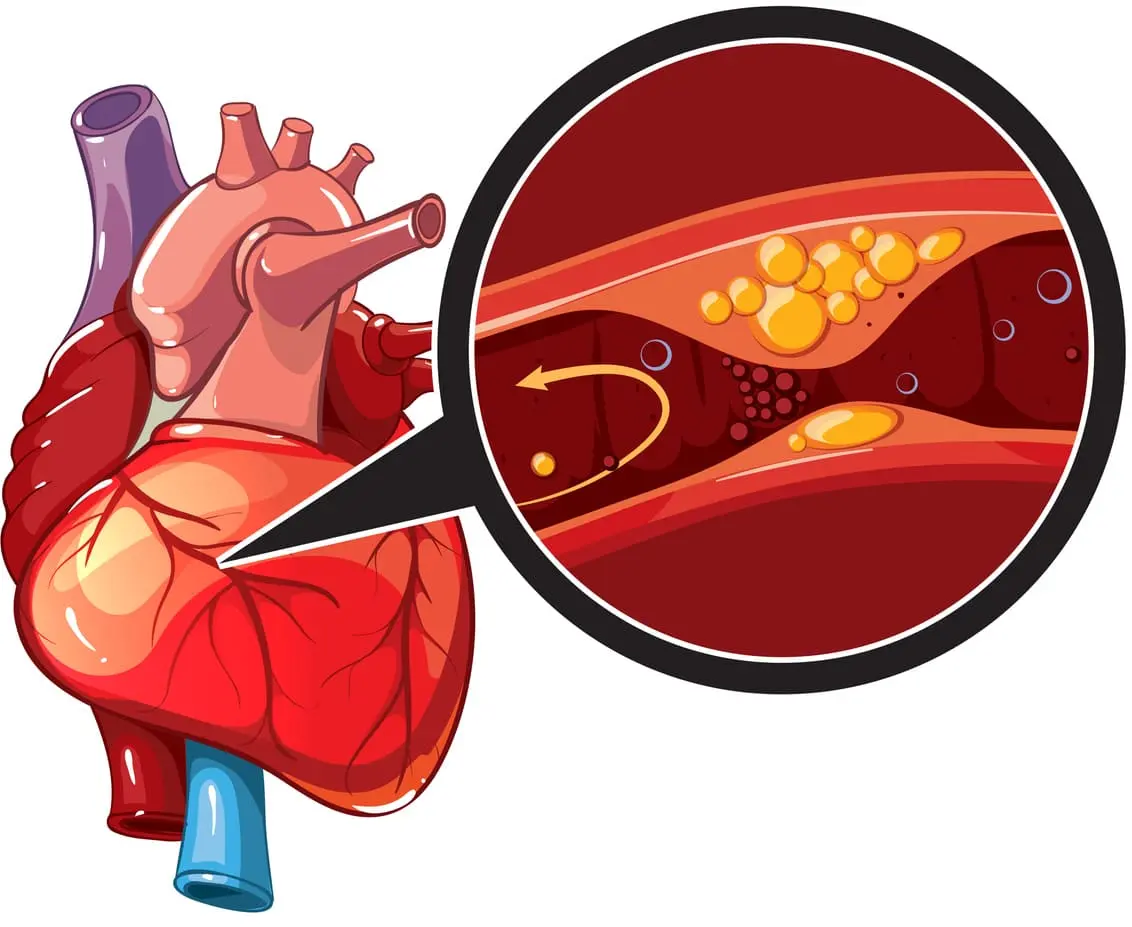
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is one of the most common and serious cardiovascular conditions worldwide. It occurs when the coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of fatty deposits (plaques). This process, called atherosclerosis, reduces blood flow to the heart, leading to chest pain, shortness of breath, or even heart attacks.
Coronary artery disease progresses gradually over years, often without noticeable symptoms until the narrowing becomes severe. It is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality across the globe and is considered a major lifestyle-related disease. The condition does not only impact physical health but also affects the overall quality of life, making timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment essential.
At DMPhysios, a Noida-based clinic specializing in spine and sports conditions, the approach to rehabilitation always emphasizes patient-centered care. While DMPhysios primarily deals with musculoskeletal and neurological issues, they also recognize the importance of cardiovascular health, especially when designing holistic rehabilitation programs for patients at risk of coronary artery disease.
Symptoms
The symptoms of coronary artery disease may vary from person to person. Some individuals may remain symptom-free for years, while others experience warning signs early. Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina): A classic symptom, often described as pressure, tightness, or squeezing in the chest, usually triggered by physical exertion or emotional stress.
- Shortness of breath: Occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s oxygen demand.
- Fatigue and weakness: Reduced blood flow can make even routine activities tiring.
- Pain in arms, neck, jaw, or back: Sometimes pain radiates beyond the chest.
- Heart palpitations or irregular heartbeat.
- Silent CAD: In some cases, individuals do not experience typical symptoms, and the disease is only discovered during a heart attack or routine check-up.
Recognizing these symptoms early is vital in preventing complications.
Types of Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease can present in different forms:
- Stable Angina
- Chest discomfort occurs predictably with exertion and is relieved by rest or medication.
- Unstable Angina
- Chest pain is more severe, frequent, and can occur even at rest. This is a medical emergency and indicates a high risk of heart attack.
- Silent Ischemia
- Reduced blood flow without noticeable symptoms. Detected through diagnostic tests such as ECG or stress testing.
- Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack)
- Complete blockage of a coronary artery leading to permanent damage to heart muscle.
Causes
The underlying cause of coronary artery disease is atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up inside the arteries. Several contributing factors accelerate this process:
- High cholesterol levels leading to fatty deposits in the arteries.
- High blood pressure (hypertension) which damages artery walls.
- Smoking, which contributes to arterial damage and increases clotting.
- Diabetes, which accelerates atherosclerosis.
- Obesity and unhealthy diet rich in saturated fats and processed foods.
- Sedentary lifestyle, reducing cardiovascular efficiency.
- Chronic stress, which increases blood pressure and heart strain.
Risk Factors
While anyone can develop coronary artery disease, certain risk factors make it more likely:
- Age: Risk increases after 45 in men and 55 in women.
- Family history of heart disease.
- Male gender: Men generally face a higher risk, though post-menopausal women are equally at risk.
- Unhealthy lifestyle choices like lack of exercise, poor diet, and excessive alcohol.
- Chronic medical conditions such as kidney disease or autoimmune disorders.
Treatment
The treatment of coronary artery disease focuses on improving blood flow, reducing symptoms, preventing progression, and minimizing complications like heart attacks.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy, heart-friendly diet (low in saturated fats, high in fiber and vegetables).
- Regular aerobic exercise such as walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Quitting smoking and alcohol moderation.
- Stress management through yoga, meditation, or breathing techniques.
2. Medications
- Antiplatelets (Aspirin, Clopidogrel): Prevent clot formation.
- Statins: Lower cholesterol levels.
- Beta-blockers and Calcium channel blockers: Reduce blood pressure and heart strain.
- Nitrates: Relieve chest pain.
3. Interventional / Surgical Treatments
- Angioplasty and Stent Placement: A balloon catheter opens blocked arteries and a stent keeps them open.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): A surgical procedure where blood flow is rerouted around blocked arteries.
Physiotherapy Treatment
While most people associate coronary artery disease treatment with cardiologists and surgeons, physiotherapy plays an important role in recovery and long-term management. At DMPhysios, rehabilitation programs are designed to be patient-centered, ensuring safety and gradual progression for individuals with cardiovascular risks.
Role of Physiotherapy in CAD:
- Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
- Structured exercise and lifestyle guidance under professional supervision.
- Focus on improving cardiovascular fitness, endurance, and strength.
- Aerobic Exercise Training
- Walking, cycling, and treadmill sessions to enhance oxygen delivery and heart function.
- Sessions are tailored to patient tolerance, with close monitoring of heart rate and blood pressure.
- Strength Training
- Light resistance exercises to improve muscular strength and reduce cardiovascular load.
- Breathing Exercises
- Diaphragmatic breathing and pursed-lip breathing techniques help improve oxygen efficiency and reduce anxiety.
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation (after CABG or Angioplasty)
- Gradual return to functional activities.
- Gentle mobility exercises and endurance building.
- Education on safe lifting and postural strategies.
- Stress Management and Relaxation Techniques
- Incorporation of yoga, mindfulness, and guided relaxation.
- Education and Lifestyle Counseling
- Guidance on diet, weight management, and physical activity to prevent recurrence.
At DMPhysios in Noida, physiotherapists integrate cardiac rehabilitation into a broader patient-centered rehabilitation model. This is particularly important for patients who also have musculoskeletal conditions along with coronary artery disease. The clinic ensures a multidisciplinary approach where both heart health and physical function are prioritized.
Prevention
Preventing coronary artery disease is possible through proactive lifestyle and medical strategies:
- Healthy diet: Prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Stay active: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Maintain healthy weight: Avoid obesity and central fat accumulation.
- Quit smoking: One of the most important preventive steps.
- Regular check-ups: Monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar.
- Manage stress: Incorporate relaxation, hobbies, and adequate sleep.
Conclusion
Coronary artery disease is a progressive but largely preventable and manageable condition. Early recognition of symptoms, appropriate medical intervention, and commitment to lifestyle changes can drastically reduce risks and improve outcomes. Treatment does not end with medication or surgery; long-term rehabilitation and preventive care play a crucial role.
At DMPhysios, a Noida-based clinic dedicated to spine and sports conditions, the philosophy of patient-centered rehabilitation extends to individuals with cardiovascular risks. Their structured, safe, and individualized physiotherapy programs can support patients in regaining confidence, improving fitness, and leading healthier lives even after coronary artery disease.If you or a loved one is at risk of coronary artery disease, remember that proactive steps today can prevent complications tomorrow. Reach out to DMPhysios in Noida to learn more about safe rehabilitation programs and holistic health care that put patients at the center of recovery.