Overview
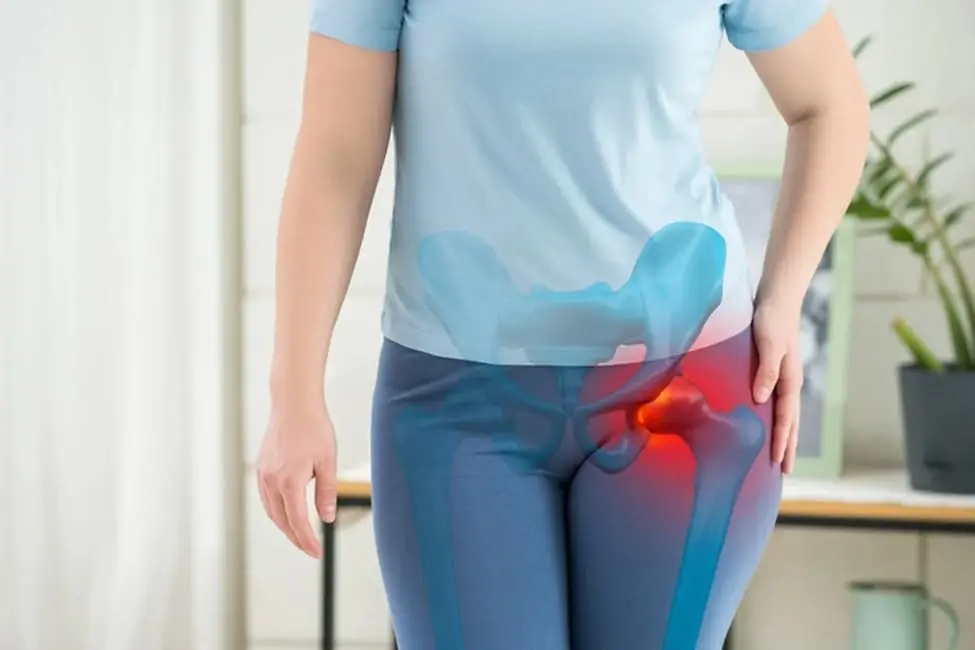
A labral tear is a complex and often debilitating injury that involves damage to the fibrocartilaginous ring—known as the labrum—that encircles the socket of ball-and-socket joints. This structure plays a critical role in stabilizing the joint, deepening the socket to secure the bone in place, and supporting smooth, pain-free movement.
Labral tears are most frequently observed in two key joints of the body: the shoulder, where the glenoid labrum lines the socket of the scapula, and the hip, where the acetabular labrum surrounds the socket of the pelvis.
When the labrum is torn—whether due to trauma, repetitive overuse, or degenerative changes—the joint’s stability and function are significantly compromised. Patients may experience a deep, persistent ache, sensations of clicking, locking, or catching within the joint, reduced mobility, and even joint weakness. These symptoms can make everyday activities like reaching overhead, walking, or rotating the joint uncomfortable or even impossible without pain.
At DMPhysios, a premier physiotherapy and rehabilitation clinic based in Noida, our expert team specializes in the assessment and treatment of labral tears through a patient-centered, evidence-informed approach. We recognize that the impact of a labral injury is not limited to elite athletes alone—office professionals, manual laborers, older adults, and recreational fitness enthusiasts are all susceptible.
That’s why we focus on individualized care plans that include detailed clinical evaluation, diagnostic support, targeted physiotherapy, and corrective exercises aimed at restoring optimal joint function. With timely intervention, expert guidance, and a structured rehabilitation plan, patients suffering from labral tears can not only return to their normal routines but also prevent future recurrence through improved strength and biomechanics.
Symptoms of a Labral Tear
The symptoms of a labral tear vary depending on whether it occurs in the shoulder or the hip. However, several hallmark signs help clinicians recognize and diagnose the condition effectively:
Common Symptoms Include:
- Deep, aching pain in the joint (shoulder or hip)
- A sensation of locking, catching, or clicking
- Decreased range of motion
- Joint instability or the feeling of the joint “giving out”
- Weakness during overhead or rotational activities (shoulder) or with weight-bearing (hip)
- Difficulty sleeping on the affected side
These symptoms can appear suddenly after trauma or develop gradually due to repetitive overuse. At DMPhysios, we ensure thorough clinical assessment and diagnostic testing, such as MRI or MR arthrogram, to confirm the presence and extent of a labral tear.
Types of Labral Tears
The classification of a labral tear largely depends on the joint involved—either the shoulder (glenoid labrum) or the hip (acetabular labrum). Each type has its own unique mechanism of injury, clinical presentation, and implications for treatment. At DMPhysios, understanding the precise type of labral tear helps us customize rehabilitation strategies that are specific, effective, and targeted for long-term joint health.
Shoulder Labral Tears (Glenoid Labrum)
The glenoid labrum is the cartilage that rims the socket of the shoulder blade (scapula), helping to hold the head of the humerus securely in place. Tears here are often the result of trauma, overuse, or instability.
1. SLAP Tear (Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior)
A SLAP tear involves a lesion in the top (superior) portion of the labrum, precisely where the biceps tendon anchors to the labral cartilage. This type of tear can occur from repetitive overhead motions—common in athletes like swimmers, baseball pitchers, and volleyball players—or from a single traumatic incident such as falling on an outstretched arm.
- Symptoms include deep shoulder pain, clicking or catching, and weakness with overhead activities.
- Subtypes (Type I to IV) classify the degree of tearing and biceps involvement.
2. Bankart Lesion
A Bankart lesion refers to a tear in the anterior-inferior part of the labrum. This usually follows a shoulder dislocation, especially in younger individuals. When the labrum detaches from the socket, it compromises joint stability and increases the risk of recurrent dislocations.
- Often seen in contact sports or traumatic falls.
- Patients may report the sensation of the shoulder “popping out” or feeling loose.
3. Posterior Labral Tear
This less common type of tear affects the back (posterior) side of the glenoid labrum. It is typically caused by repetitive posterior loading, such as during weightlifting (especially bench press) or from a direct blow to the front of the shoulder.
- May present with vague discomfort, instability, and pain during pushing movements.
Hip Labral Tears (Acetabular Labrum)
The acetabular labrum is the cartilage that surrounds the socket of the hip joint, enhancing its depth and stability. Tears in this area can develop gradually or result from acute trauma.
1. Anterior Labral Tear
The anterior labral tear is the most commonly diagnosed type of hip labral injury. It occurs at the front of the hip joint and is frequently linked with femoroacetabular impingement (FAI)—a condition in which abnormal bone shapes rub against the labrum during movement.
- Often caused by repetitive twisting, pivoting, or prolonged sitting.
- Common in athletes such as runners, soccer players, and martial artists.
2. Posterior Labral Tear
A posterior tear affects the back portion of the acetabular labrum. Though less frequent, it may arise due to repetitive hip hyperextension or sudden backward loading, such as in ballet or gymnastics.
- Symptoms include deep buttock pain, instability, and occasional joint locking.
3. Degenerative Labral Tear
Degenerative tears are most often seen in middle-aged to older adults and result from the gradual breakdown of the labrum over time. These are commonly associated with underlying osteoarthritis or joint wear due to poor biomechanics or chronic overload.
- Onset is typically insidious with stiffness, dull aching, and occasional mechanical symptoms.
- Treatment may also focus on managing co-existing arthritic changes.
At DMPhysios, we take the time to classify each labral tear not just by location, but also by underlying cause, patient activity level, and biomechanical risk factors. This comprehensive approach ensures that rehabilitation is not only effective for healing the current injury but also preventive against future recurrence. Whether it’s a SLAP tear in a swimmer or an anterior labral tear in a long-distance runner, our Noida-based clinic offers expert care tailored to your specific presentation.
Causes of Labral Tear
A labral tear may result from a variety of factors, including acute trauma or repetitive joint motion. Some common causes include:
- Trauma or direct impact: Falls, sports collisions, or motor vehicle accidents.
- Repetitive motion injuries: Especially common in swimmers, baseball pitchers, gymnasts, and dancers.
- Joint dislocations or subluxations: Often seen in contact sports.
- Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI): Causes abnormal hip mechanics leading to labral damage.
- Age-related degeneration: Cartilage wears out over time, increasing susceptibility to labral injury.
Understanding the root cause of your labral tear is crucial to selecting the appropriate treatment. At DMPhysios, we perform biomechanical assessments to identify movement faults contributing to injury and design rehabilitation plans that address them.
Risk Factors
While a labral tear can affect anyone, several risk factors increase the likelihood:
- High-impact sports participation (rugby, football, hockey)
- Overhead or rotational activities (swimming, tennis, baseball)
- Previous joint dislocation or subluxation
- Congenital structural abnormalities like hip dysplasia or shoulder instability
- Poor joint biomechanics
- Inadequate warm-up or muscle imbalances
- Age and joint degeneration
At DMPhysios, we educate patients on how to minimize these risk factors through personalized training and injury prevention strategies.
Treatment of Labral Tear
Treatment for a labral tear depends on the severity of the damage, the patient’s activity level, and whether the tear is causing mechanical symptoms.
Non-Surgical Treatment:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding aggravating activities like overhead lifting or high-impact sports.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help manage pain and swelling.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, to reduce inflammation and pain in the joint.
- Physiotherapy: Core component of conservative management, especially for minor to moderate tears.
Surgical Options:
Surgery is considered when conservative management fails. It may include:
- Labral Debridement: Trimming the frayed or damaged labral tissue.
- Labral Repair: Reattaching the torn labrum using sutures and anchors.
- Addressing structural causes: Like bone reshaping in FAI to prevent recurrence.
At DMPhysios, we collaborate with orthopedic surgeons in Noida and offer post-operative rehabilitation to ensure smooth recovery after labral repair surgeries.
Physiotherapy Treatment
Physiotherapy plays a pivotal role in both non-surgical and post-surgical treatment of labral tears. At DMPhysios, we follow a patient-centered rehabilitation model grounded in clinical expertise, movement science, and functional goals.
Phase 1: Pain and Inflammation Control
- Cryotherapy
- Joint offloading techniques
- Taping or bracing (if needed)
- Gentle isometric exercises
- Education on movement avoidance and activity modification
Phase 2: Mobility Restoration
- Passive and active-assisted range of motion exercises
- Gentle joint mobilizations
- Soft tissue release (manual therapy) for tight structures
- Capsular stretching techniques (especially in hip labral tears)
Phase 3: Strengthening and Stabilization
- Rotator cuff and scapular muscle strengthening (shoulder labral tear)
- Gluteal and core strengthening (hip labral tear)
- Resistance bands and closed-chain exercises
- Proprioceptive and neuromuscular control training
Phase 4: Functional Integration
- Sport-specific drills
- Plyometric training
- Agility and coordination exercises
- Movement retraining and correction of faulty biomechanics
Phase 5: Return to Sport or Activity
- Criteria-based progression
- Objective strength and function testing
- Return-to-play decision making in collaboration with orthopedic teams
At DMPhysios, our physiotherapists customize these protocols to individual needs and continuously monitor progress using outcome measures. Whether you’re a swimmer with a shoulder labral tear or a dancer with a hip labral tear, we offer evidence-based, one-on-one care to guide your full recovery.
Prevention of Labral Tears
Preventing a labral tear involves addressing joint mechanics, muscle imbalances, and training habits:
- Warm-Up Properly: Dynamic stretching and mobility drills before activity
- Strength Training: Build stability around the joint, especially rotator cuff and core
- Avoid Repetitive Stress: Modify training to prevent overuse
- Improve Movement Patterns: Especially during sports or functional activities
- Use Correct Technique: Whether in sports, lifting, or dance
- Posture Correction: Essential for shoulder and hip joint alignment
- Regular Check-Ups at DMPhysios: Early detection of imbalance or dysfunction
Conclusion
A labral tear, whether in the hip or shoulder, can significantly limit your mobility, comfort, and performance. But with early diagnosis, targeted treatment, and structured physiotherapy, most individuals can return to their previous level of function—and often, even better.
At DMPhysios, located in Noida, we take pride in delivering patient-centered rehabilitation that addresses not just the injury, but the individual behind it. Whether you’re managing a chronic labral tear or recovering from surgery, our expert physiotherapists guide you through every stage of your healing journey.
Don’t let a labral tear define your movement. Contact DMPhysios today for an expert consultation, personalized assessment, and a dedicated recovery plan. Our goal is to get you moving better, faster, and stronger—with compassion and science at the core.
Book your appointment with DMPhysios, Noida’s trusted spine and sports rehab clinic, and take control of your healing journey today!