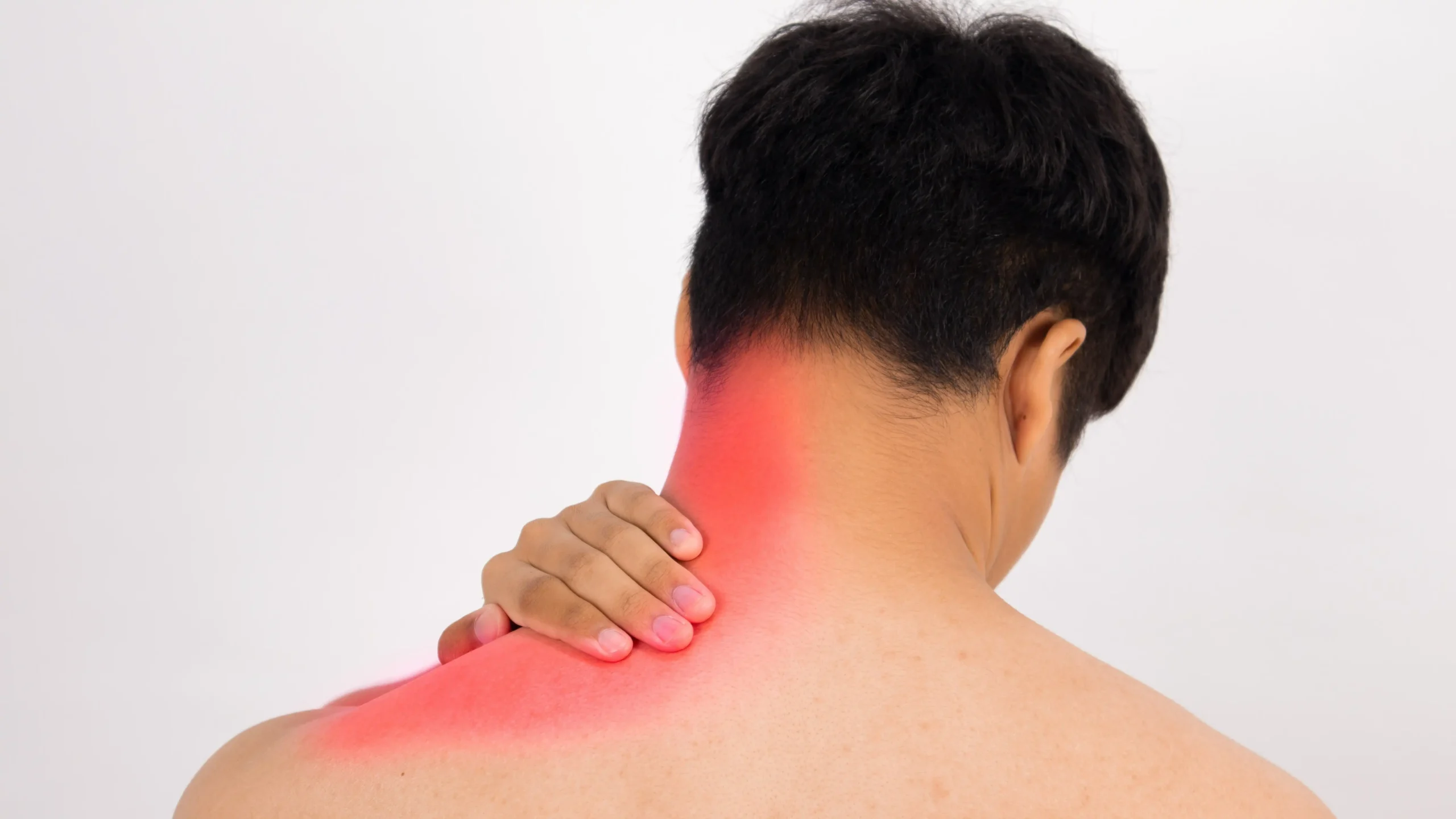
Core Strengthening and Back Pain:
How Strengthening of the Core helps in Relieving Back Pain
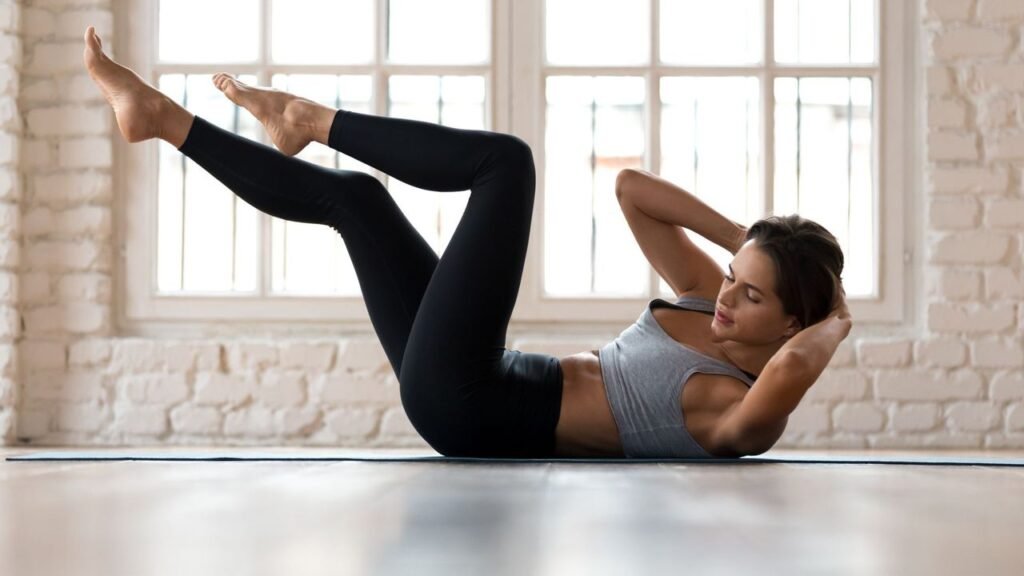
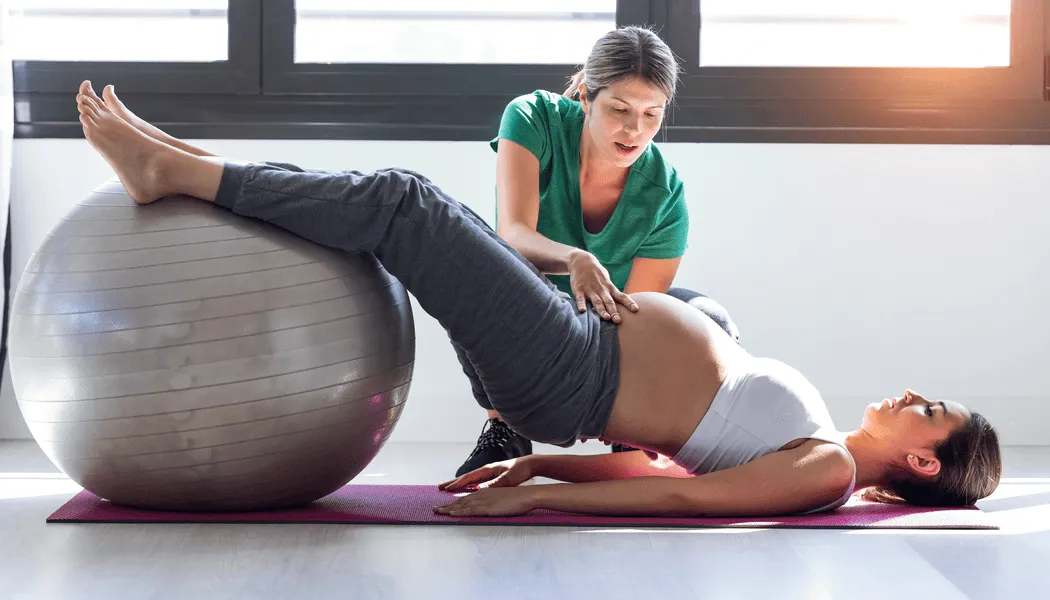
C ore strengthening and core stability exercises are the most effective ways to manage and alleviate lower back pain (LBA). By strengthening the muscles around the lower spine and pelvis, these exercises help reduce pain, lower the risk of injury, and enhance balance, stability, and endurance. Consistent practice improves muscle coordination, supports better posture, and promotes mobility. Together, these benefits can boost confidence and significantly enhance overall quality of life.
What is " THE CORE" ?
The Core is located at the center of your body and consists of a deep layer of muscles that support the spine, buttocks, back, hips, and abdomen. These muscles play a vital role in maintaining strong and upright posture, enabling you to bend, twist, run, jump, and move with ease.
The Core muscles, which serve as the primary muscle group for maintaining spinal stability, can be divided into two groups based on their functions and attributes.
The First Group consists of the deep core muscles, also known as local stabilizing muscles. These include:
1. Transversus abdominis
2. Lumbar multifidus
3. Internal oblique
4. Quadratus lumborum
The Second Group of core muscles consists of the shallow core muscles, also referred to as global stabilizing muscles.
This group includes:
1. Rectus abdominis
2. Internal and External obliques
3. Erector spinae
4. Quadratus lumborum
5. Muscles of the hips
When functioning properly, the core muscles maintain segmental stability, protect the spine, and reduce stress on the lumbar vertebrae and intervertebral discs. For this reason, the core muscles are often referred to as ‘the natural brace’ of the human body.
What is the Relationship between Core Strength and Back Pain?
The main function of the core muscle is to hold the spine straight, maintain its curvature, distribute the weight evenly , spine stability and reduce stress on the passive structure around the spine.
When the core muscles get weak, the back doesn’t support the weight and is not able to distribute the weight accordingly.
As a result, core muscles fail to provide adequate balance, stability, and control, the spine and back muscles are forced to overcompensate. This overexertion places additional strain on these structures and also involves the passive structures i e ligaments, bones or disc that is present between the 2 vertebrae which can lead to discomfort, muscle fatigue, and chronic back pain over time.
Although the symptoms of lower back pain can differ from person to person, the pain is commonly described as:
- A dull or nagging ache
- Sharp pain after standing
- A stabbing or shooting sensation.
- A sharp, stinging, tingling, or numb feeling that radiates down the thighs into the lower legs and feet.
How Core Strengthening Exercises Help with Lower Back Pain:
1. Improve Spinal Stability: Core Strengthening exercises increase spinal stiffness and reduce instability, helping you maintain mobility and recover more quickly.
2. Reduce Pain: Regular core strengthening can alleviate the intensity of back pain.
3. Improve Posture: These exercises enhance the coordination between your core muscles and other body parts, leading to better posture.
4. Reduce Risk of Injury: Strengthening the core can help prevent strains and sprains by stabilizing the body.
5. Improve Balance: Core Strengthening exercises boost balance and stability, improving overall movement control.
6. Enhanced Functional Movement: Core strengthing are crucial for everyday activities such as lifting, bending, and twisting. A strong core makes these movements easier and more efficient, reducing the risk of back injuries.
7. Reduced Muscle Imbalances: Engaging the core muscles helps distribute stress evenly across the body, preventing imbalances that can contribute to back pain.