Physiotherapy Curriculum Reform 2025
How India’s New Standards Will Shape Future Professionals
Article Overview
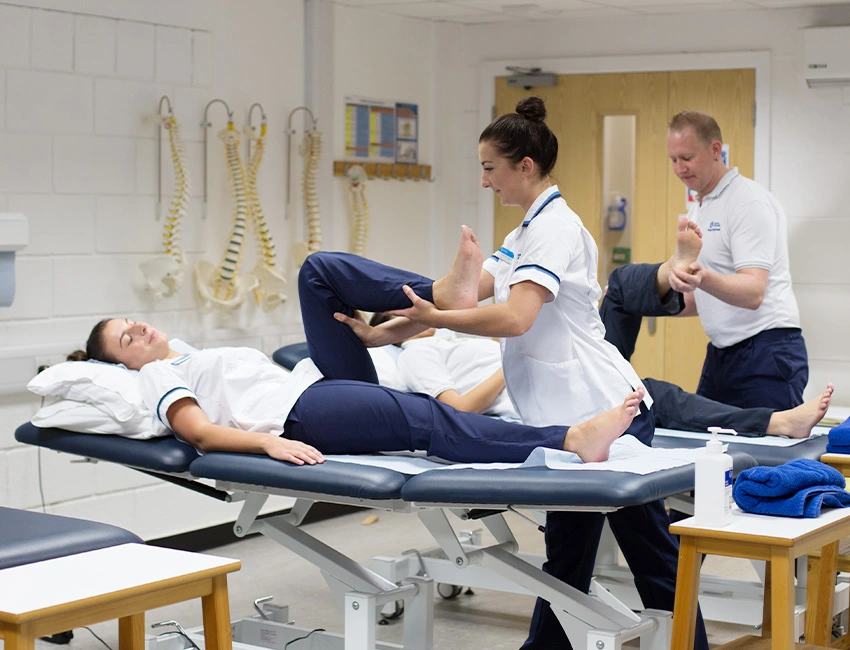
Physiotherapy has long been one of the most vital pillars of healthcare in India. What began decades ago as an allied support service is today recognized as an independent, evidence-based profession that restores mobility, prevents disability, and enhances quality of life. From athletes recovering from injuries to elderly patients regaining independence after a stroke, physiotherapists are central to healing and rehabilitation.
As India moves into 2025, the profession is about to witness a landmark change—the Physiotherapy Curriculum Reform 2025. This reform represents more than just revised syllabi; it is a bold step towards raising educational standards, integrating modern healthcare needs, and aligning Indian physiotherapy with global benchmarks.
This article explores why the reform was needed, what it introduces, and how it will shape the next generation of physiotherapists.
Why a Curriculum Reform Was Needed
Healthcare in India has transformed rapidly in the last 20 years. With lifestyle diseases, sedentary habits, workplace injuries, and an ageing population on the rise, the demand for physiotherapy has skyrocketed. Yet, many academicians and practitioners have raised concerns about the gaps in existing Physiotherapy Curriculum.
Key challenges have included:
- Outdated Physiotherapy Curriculum syllabi with minimal updates to reflect modern practices.
- Limited integration of technology despite global advances in rehabilitation robotics, telehealth, and virtual reality.
- Insufficient research orientation, leaving graduates less prepared for evidence-based practice.
- Variability in quality across institutions, creating inconsistencies in professional competency.
- Minimal focus on soft skills such as patient communication, counselling, and inter-professional collaboration.
Recognizing these challenges, policymakers, educators, and physiotherapy councils initiated the Curriculum Reform 2025, a forward-looking framework to make physiotherapy education more robust, relevant, and globally competitive.
Key Features of the 2025 Reform
The reform introduces several significant updates that will reshape physiotherapy training in India.
1. Evidence-Based Learning as Core Philosophy
The revised curriculum places critical thinking, research evaluation, and clinical reasoning at its heart. Instead of rote-based learning, students will be trained to apply evidence-based methods in patient care, ensuring that interventions are both scientific and outcome-driven.
2. Technology-Driven Rehabilitation Training
Modern physiotherapy increasingly involves tools such as:
- Robotic exoskeletons for gait training
- Virtual reality platforms for balance and coordination
- Artificial intelligence in movement assessment
The curriculum ensures that graduates are trained in these tools, preparing them to work in technologically advanced hospitals and sports science facilities.
3. Expanded Clinical Rotations
Students will now undergo structured clinical postings across a wider range of specialties: orthopaedics, neurology, cardiopulmonary rehabilitation, sports medicine, geriatrics, women’s health, paediatrics, and community physiotherapy. This broad-based exposure will ensure professionals are competent across diverse patient groups.
4. Research and Academic Contributions
Every student will engage in meaningful research projects and publications. By cultivating a research-driven mindset, the reform ensures that physiotherapists contribute actively to new discoveries and innovations in rehabilitation science.
5. Soft Skills and Patient Interaction
Recognizing that physiotherapists often serve as educators and motivators, the curriculum now includes modules on:
- Patient education and counselling
- Motivational interviewing
- Cultural sensitivity in healthcare
- Collaborative teamwork in multidisciplinary settings
6. Tele-Rehabilitation and Digital Care
One of the most progressive additions is the integration of tele-rehabilitation training. With India’s vast rural population, physiotherapists will be trained to deliver consultations, monitor progress, and guide therapy remotely—bridging gaps in healthcare access.
7. Global Alignment
The reforms bring Indian physiotherapy education closer to international guidelines set by the World Confederation for Physical Therapy (WCPT). This alignment boosts global recognition, mobility, and career opportunities for Indian physiotherapists.
What This Means for Students
For aspiring physiotherapists, the new standards bring immense opportunities:
- Stronger career readiness: Graduates will be equipped with practical skills that employers demand.
- Access to global pathways: Internationally aligned training opens doors to research, higher education, and practice abroad.
- Entrepreneurial potential: With training in digital health, graduates can establish their own practices and tele-consultation services.
Lifelong adaptability: Evidence-based learning ensures that professionals stay relevant even as healthcare evolves.
What This Means for the Profession
The Physiotherapy Curriculum Reform 2025 elevates the status of physiotherapists as frontline healthcare providers. Its wider impact includes:
- Recognition as essential healthcare contributors in hospitals, sports, and community care.
- Enhanced credibility within multidisciplinary teams, where physiotherapists often lead rehabilitation planning.
- Stronger voice in public health policies, especially regarding lifestyle diseases, disability prevention, and elderly care.
- Growth of specialized branches like sports science, ergonomics, neuro-rehabilitation, and women’s health physiotherapy.
Challenges to Implementation
While the vision is ambitious, certain challenges must be addressed:
- Faculty training: Educators need to update themselves in research and modern rehabilitation technologies.
- Infrastructure requirements: Colleges must invest in simulation labs, digital platforms, and modern equipment.
- Standardization: Ensuring uniform quality across urban and rural institutions remains a challenge.
- Balancing workload: The curriculum must remain rigorous without overwhelming students.
Physiotherapy in India’s Healthcare Future
India’s healthcare demands are expanding, and physiotherapists will play a critical role in:
- Preventive healthcare: Educating communities on posture, ergonomics, and exercise.
- Post-surgical rehabilitation: Enabling faster recovery after joint replacements, cardiac surgeries, or neurosurgeries.
- Neurological rehabilitation: Supporting stroke, spinal cord injury, and cerebral palsy patients.
- Sports rehabilitation and performance: Preventing injuries and enhancing performance in athletes.
- Geriatric and paediatric care: Supporting vulnerable populations with long-term conditions.
With the new curriculum, physiotherapists will be trained not just as clinicians, but as innovators, researchers, and leaders shaping healthcare delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Conclusion
The Physiotherapy Curriculum Reform 2025 is a milestone in Indian healthcare education. By integrating technology, evidence-based practice, research, and soft skills, it ensures that the next generation of physiotherapists will be globally competent, locally relevant, and patient-centered.
For students, it opens new pathways. For patients, it promises better quality of care. And for the nation, it strengthens one of the most important aspects of healthcare—movement and rehabilitation.
Physiotherapy in India is entering a new era—one where its professionals will not only heal but also lead, innovate, and transform the healthcare landscape.